Preliteracy Skills in Young Children Who are Deaf/Hard of Hearing: Secondary Analysis of the Technology-assisted Language Intervention Randomized Trials
- PMID: 40700591
- PMCID: PMC12378878
- DOI: 10.1097/DBP.0000000000001394
Preliteracy Skills in Young Children Who are Deaf/Hard of Hearing: Secondary Analysis of the Technology-assisted Language Intervention Randomized Trials
Abstract
Objectives: Most children exhibit preliteracy skills by preschool. Children who are deaf/hard of hearing (DHH) with a language gap are at risk for delayed preliteracy skills. Our study aimed to describe preliteracy skill development in preschool-aged DHH children and investigate associated factors.
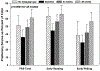
Methods: Children, aged 3 to 5 years, were included in the analysis if enrolled in randomized trials of a language intervention using augmentative and alternative communication, shown to boost language skills. Evaluations using the Clinical Evaluations of Fundamentals-Preschool Preliteracy Rating Scale (PRS) were conducted at baseline, 24 weeks, and 48 weeks. Repeated-measures models assessed changes in total PRS scores and Early Reading and Early Writing subdomains. Results were presented as least square mean values with 95% confidence intervals.
Results: Forty-five children had completed pre-data and post-data. The mean nonverbal IQ was 99.3 (SD 14.3), and receptive and expressive language were 82.3 (14.9) and 76.8 (17.0), respectively. Significant (p < 0.0001) skill growth was observed with all preliteracy outcomes, ranging from 11 to 15 points in the first 24 weeks. Increasing receptive and expressive language over time was significantly associated with increasing scores. Factors such as aided hearing thresholds, caregiver education level, and hearing device use were not significant in models.
Conclusion: Language is essential for literacy development. Language-enhancing interventions could facilitate literacy skills. Monitoring preliteracy skills in DHH children is crucial, given their increased risk for language delays. Further research is needed to support early literacy development in this population, ensuring they have the tools they need for future success.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02998164.
Keywords: deaf and hard of hearing; language; preliteracy skills.
Copyright © 2025 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Screening for speech and language delay in preschool children: systematic evidence review for the US Preventive Services Task Force.Pediatrics. 2006 Feb;117(2):e298-319. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-1467. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 16452337
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
A randomised controlled trial of the effectiveness of parent-based models of language intervention for 2- to 3-year-old children with speech, language and communication needs (SLCN) in areas of social disadvantage.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024 Jul-Aug;59(4):1517-1537. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.13016. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024. PMID: 38285603 Clinical Trial.
-
The agreement of phonetic transcriptions between paediatric speech and language therapists transcribing a disordered speech sample.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024 Sep-Oct;59(5):1981-1995. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.13043. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024. PMID: 38850167
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sénéchal M, LeFevre JA. Parental involvement in the development of children’s reading skill: a five-year longitudinal study. Child Dev. 2002;73:445–460. - PubMed
-
- National Early Literacy Panel. Developing Early Literacy: Report of the National Early Literacy Panel. Washington, DC: National Institute for Literacy; 2008.
-
- Dirks E, Wauters L. It takes two to read: interactive reading with young deaf and hard-of-hearing children. J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2018;23:261–270. - PubMed
-
- Spencer PE, Marschark M. Evidence-based Practices in Educating Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2010.
-
- Lederberg AR, Schick B, Spencer PE. Language and literacy development of deaf and hard-of-hearing children: successes and challenges. Dev Psychol. 2013;49:15–30. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

