NMR Spectroscopy-Based Lipoprotein and Glycoprotein Biomarkers Differentiate Acute and Chronic Inflammation in Diverse Healthy and Disease Population Cohorts
- PMID: 40700744
- PMCID: PMC12322961
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5c00300
NMR Spectroscopy-Based Lipoprotein and Glycoprotein Biomarkers Differentiate Acute and Chronic Inflammation in Diverse Healthy and Disease Population Cohorts
Abstract
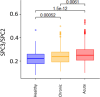
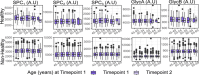
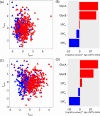
Understanding the distribution and variation in NMR-based inflammatory markers is crucial to the evaluation of their clinical utility in disease prognosis and diagnosis. We applied high-resolution 1H NMR spectroscopy of blood plasma and serum to measure the acute phase reactive glycoprotein signals (GlycA and GlycB) and the subregions of the lipoprotein-based Supramolecular Phospholipid Composite signals (SPC1, SPC2, and SPC3) in a large multicohort population study. A total of 5702 samples were studied to determine the signal variations in a range of chronic and acute inflammatory conditions. We found that while GlycA and GlycB were increased in inflammation, the SPC regions behaved independently of Glyc signals, with SPC2 and SPC3 being reduced in chronic inflammation in comparison to healthy controls (p-value SPC2 = 2.9 × 10-10, p-value SPC3 = 2.2 × 10-3) and SPC1 (p-value = 0.29) being unchanged. SPC1 was decreased in acute inflammation, indicating a link to the immune response (p-value = 2.5 × 10-11). These findings confirm the independent biological relevance of all three SPC subregions and contraindicate the use of aggregate SPC values as general inflammatory markers.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; NMR spectroscopy; SARS-CoV-2; SPC; Supramolecular Phospholipid Composite signals; acute inflammation; blood plasma metabolic phenotyping; cardiovascular disease risk; chronic inflammation; diabetes; glycoproteins; inflammation.
Figures


References
-
- Lodge S., Nitschke P., Kimhofer T., Coudert J. D., Begum S., Bong S.-H., Richards T., Edgar D., Raby E., Spraul M., Schaefer H., Lindon J. C., Loo R. L., Holmes E., Nicholson J. K.. NMR Spectroscopic Windows on the Systemic Effects of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Plasma Lipoproteins and Metabolites in Relation to Circulating Cytokines. J. Proteome Res. 2021;20:1382–1396. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00876. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

