Data sharing statements for clinical trials: a cross-sectional survey of cardiology journals
- PMID: 40701601
- PMCID: PMC12306300
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-097148
Data sharing statements for clinical trials: a cross-sectional survey of cardiology journals
Abstract
Objective: The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors requires data sharing statements in trial publications, but whether cardiology journals request data sharing statements in clinical trial submissions is unclear. We performed a survey to assess whether cardiology journals request data sharing statements in clinical trials.
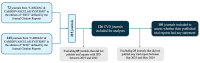
Design, setting, data source and participants: All cardiac and cardiovascular systems journals that published clinical trials from January 2019 to December 2022 were included. The study outcome was journal requests for data sharing statements. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to examine the association between journal characteristics and journal requests. We also explored whether journal requests aligned with their subsequently published clinical trials.
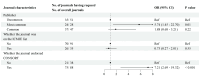
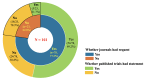
Results: A total of 126 journals were included, among which 96 (76.2%) requested data sharing statements in clinical trials. Elsevier journals and Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials endorsement had increased adjusted odds of requesting data sharing statements, with an OR of 5.74 (95% CI 1.45 to 22.70) and 7.21 (2.69 to 19.32), respectively. In the 78 journals that requested statements, 24 (30.8%) indeed did not publish any data sharing statement in their trial reports.
Conclusions: Approximately one in four cardiology journals did not request data sharing statements on clinical trial submissions, while a substantial inconsistency existed between journal requests and the actual publications of statements in their published trial reports.
Keywords: CARDIOLOGY; Clinical Trial; Health informatics; Surveys and Questionnaires.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consolidated standards of reporting trials (CONSORT) and the completeness of reporting of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) published in medical journals.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11(11):MR000030. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000030.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23152285 Free PMC article.
-
Publication of data sharing statements in clinical trials by cardiovascular journals: a quantitative and qualitative analysis.Sci Data. 2025 Jul 15;12(1):1239. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05510-x. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40664672 Free PMC article.
-
Do peer reviewers comment on reporting items as instructed by the journal? A secondary analysis of two randomized trials.J Clin Epidemiol. 2025 Jul;183:111818. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2025.111818. Epub 2025 May 8. J Clin Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40348145
-
Data-Sharing Statements Requested from Clinical Trials by Public, Environmental, and Occupational Health Journals: Cross-Sectional Study.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Feb 7;27:e64069. doi: 10.2196/64069. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39919275 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials of pharmacologic treatment of bipolar disorders: a systematic review.J Clin Psychiatry. 2011 Sep;72(9):1214-21. doi: 10.4088/JCP.10r06166yel. Epub 2011 Jan 25. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21294992
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
