Effectiveness of ixekizumab in 709 real-world patients with axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis: a nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 40701624
- PMCID: PMC12306273
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005806
Effectiveness of ixekizumab in 709 real-world patients with axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis: a nationwide cohort study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Effectiveness of ixekizumab in 709 real-world patients with axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis: a nationwide cohort study.RMD Open. 2025 Aug 12;11(3):e005806corr1. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005806corr1. RMD Open. 2025. PMID: 40803823 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: To explore real-world effectiveness of ixekizumab in Danish patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: Observational cohort study based on data from the Danish nationwide quality registry, DANBIO. Patients with axSpA and PsA initiating ixekizumab (an interleukin 17 inhibitor (IL-17i)) between 2017 and 2024 were included. Outcomes were 6-, 12- and 24-month retention rates and low disease activity (LDA)/remission after 6 months (axSpA: Axial Spondyloarthritis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) <2.1/<1.3, PsA: Disease Activity index for Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA28) ≤14/≤4, respectively). Clinical factors associated with retention were explored (multivariable Cox regression analyses with adjusted HRs (aHRs)).
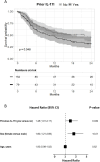
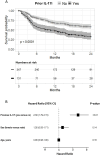
Results: 709 patients were included (axSpA: 231, PsA: 478). Most patients were bio-experienced (axSpA: 97%, PsA: 91%). The 6-, 12- and 24-month retention rates were for axSpA: 69% (95% CI 63; 76), 53% (46; 60) and 40% (33; 49); for PsA: 75% (71; 79), 63% (58; 67) and 51% (46; 57), respectively. Patients previously treated with another IL-17i (axSpA 36%, PsA 34%) had an increased risk of withdrawal (aHR: axSpA 1.48 (1.01; 2.17), PsA 2.38 (1.79; 3.15)). Smoking, radiographic status (axSpA) or concomitant methotrexate (PsA) were not associated with withdrawal. After 6 months, 24% of axSpA patients had ASDAS-LDA, and 5% were in ASDAS-remission. For PsA, DAPSA28-LDA was achieved in 43% and DAPSA28-remission in 10%, respectively.
Conclusion: In this nationwide observational study, ixekizumab was primarily prescribed in patients who had failed multiple biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs), including other IL-17i. Retention rates were somewhat lower for axSpA than for PsA. For both axSpA and PsA, prior IL-17i treatment was associated with an increased risk of withdrawal, yet the relatively high retention rate and improvement in all disease activity outcomes suggest ixekizumab as a viable option for patients with multiple b/tsDMARD failures.
Keywords: Axial Spondyloarthritis; DMARD; Interleukin-17; Psoriatic Arthritis; Treatment.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KYJ: none declared. KLG: none declared. MLH: research grant (paid to institution): AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly, MSD, Pfizer and Sandoz, Novartis, UCB; speaker’s fee (paid to institution): Medac, Pfizer and Sandoz. Speaker’s fee (personal): Novartis. BG: research grants (paid to institution): Pfizer, AbbVie, Sandoz, BMS and Eli Lilly. Chairs the DANBIO steering committee.
Figures

References
-
- Aksial spondylartritis | danskreumatologi.dk. [25-Jun-2025]. https://danskreumatologi.dk/nbv/sygdomme/aksial-spondyloartritis/ Available. Accessed.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
