Advancements and challenges in inverse lithography technology: a review of artificial intelligence-based approaches
- PMID: 40701983
- PMCID: PMC12287475
- DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01923-w
Advancements and challenges in inverse lithography technology: a review of artificial intelligence-based approaches
Abstract
Inverse lithography technology (ILT) is a promising approach in computational lithography to address the challenges posed by shrinking semiconductor device dimensions. The ILT leverages optimization algorithms to generate mask patterns, outperforming traditional optical proximity correction methods. This review provides an overview of ILT's principles, evolution, and applications, with an emphasis on integration with artificial intelligence (AI) techniques. The review tracks recent advancements of ILT in model improvement and algorithmic efficiency. Challenges such as extended computational runtimes and mask-writing complexities are summarized, with potential solutions discussed. Despite these challenges, AI-driven methods, such as convolutional neural networks, deep neural networks, generative adversarial networks, and model-driven deep learning methods, are transforming ILT. AI-based approaches offer promising pathways to overcome existing limitations and support the adoption in high-volume manufacturing. Future research directions are explored to exploit ILT's potential and drive progress in the semiconductor industry.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

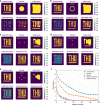
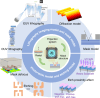


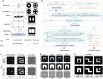
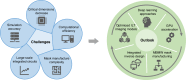
References
-
- Wang, Y. B. et al. Photonic-circuit-integrated titanium: sapphire laser. Nat. Photonics17, 338–345 (2023).
-
- El Helou, C. et al. Mechanical integrated circuit materials. Nature608, 699–703 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 62235009/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- 62235009/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- 62235009/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- 62235009/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- 62235009/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

