Blockchain framework with IoT device using federated learning for sustainable healthcare systems
- PMID: 40701986
- PMCID: PMC12287362
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06539-z
Blockchain framework with IoT device using federated learning for sustainable healthcare systems
Abstract
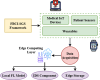
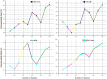
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) sector has advanced rapidly in recent years, and security and privacy are essential considerations in the IoMT due to the extensive scope and implementation of IoMT networks. Machine learning (ML) and blockchain (BC) technologies have dramatically improved the functionalities and services of Healthcare 5.0, giving rise to a new domain termed Smart Healthcare. A proactive healthcare system may prevent long-term harm by recognizing issues early. This would improve patients' quality of life while alleviating their worry and healthcare expenses. The IoMT facilitates several capabilities in information technology, including intelligent and interactive healthcare. Consolidating medical information into a singular repository to train a robust ML model engenders apprehensions around privacy, ownership, and adherence to regulatory standards due to increased concentration. Federated learning (FL) addresses previous challenges using a centralized aggregate server to distribute global learning models. The local participant controls patient data, ensuring data confidentiality and security. Hence, this study proposes the Federated Blockchain-IoT Framework for Sustainable Healthcare Systems (FBCI-SHS) for a secure health monitoring system. Additionally, this paper presents the Intrusion Detection System (IDS) as a tool for healthcare network intrusion detection, allowing doctors to track patients' vitals using medical sensors and anticipate when they could become sick so they can take preventative steps. The suggested system proves that the method is well-suited for medical monitoring. In contrast, the high prediction accuracy for intrusion detection and the high efficiency in disease detection achieved by the proposed FBI-SHS healthcare 5.0 system. The proposed method achieves data privacy and security by 98.73%, intrusion detection efficiency by 97.16%, disease detection accuracy by 96.425, proactive healthcare management by 98.37%, and interoperability by 96.74%.
Keywords: Blockchain; Federated learning; Internet of things (IoT); Intrusion detection system; Monitoring system; Smart healthcare; Sustainable healthcare systems.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Fused federated learning framework for secure and decentralized patient monitoring in healthcare 5.0 using IoMT.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 7;15(1):24263. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06574-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40624105 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying significant features in adversarial attack detection framework using federated learning empowered medical IoT network security.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 26;15(1):31485. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14913-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40858640 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating IoMT and Federated Learning for Advanced Healthcare Monitoring in Healthcare 5.0.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 8. doi: 10.2174/0113892010380715250728143022. Online ahead of print. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40798954
-
Technologies for Interoperable Internet of Medical Things Platforms to Manage Medical Emergencies in Home and Prehospital Care: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 23;27:e54470. doi: 10.2196/54470. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39847768 Free PMC article.
-
Blockchain Integration With Digital Technology and the Future of Health Care Ecosystems: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Nov 2;23(11):e19846. doi: 10.2196/19846. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34726603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed, I. et al. A blockchain-and artificial intelligence‐enabled smart IoT framework for sustainable City. Int. J. Intell. Syst.37 (9), 6493–6507 (2022).
-
- Reegu, F. A. et al. Blockchain-based framework for interoperable electronic health records for an improved healthcare system. Sustainability15 (8), 6337 (2023).
-
- Arun, M. et al. Internet of things and deep learning-enhanced monitoring for energy efficiency in older buildings. Case Stud. Therm. Eng.61, 104867 (2024).
-
- Vishwakarma, A., Dangayach, G. S., Meena, M. L., Gupta, S. & Luthra, S. Adoption of blockchain technology enabled healthcare sustainable supply chain to improve healthcare supply chain performance. Manage. Environ. Quality: Int. J.34 (4), 1111–1128 (2023).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

