Homeostatic scaling of dynorphin signaling by a non-canonical opioid receptor
- PMID: 40701991
- PMCID: PMC12287315
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62133-x
Homeostatic scaling of dynorphin signaling by a non-canonical opioid receptor
Abstract
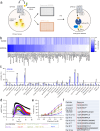
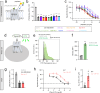
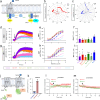
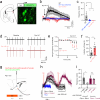
The endogenous opioid system provides powerful control over emotions, nociception, and motivation among many other fundamental nervous system functions. Its major components include a panel of opioid peptides that activate four canonical inhibitory opioid receptors. However, its regulatory principles are not fully understood including the existence of additional receptors and other elements. In this study we report the identification of a receptor for the opioid peptide dynorphin. By conducting a screen of a custom library of neuropeptides, we found that orphan receptor GPR139 binds to and is activated by a series of dynorphin peptides. Unlike other opioid receptors, GPR139 couples to Gq/11 and avoids β-arrestin, providing excitatory signaling that homeostatically scales the inhibitory response of neurons to dynorphin. This introduces a non-canonical dynorphin receptor as an essential component of the opioid system.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: K.A.M. is a consultant and stakeholder in EvoDenovo, Inc. a company commercializing the development of innovative treatments for opioid use disorder. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- D’Amato, F. R. & Pavone, F. Modulation of nociception by social factors in rodents: contribution of the opioid system. Psychopharmacology224, 189–200 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Gavériaux-Ruff, C. & Kieffer, B. L. Opioid receptor genes inactivated in mice: the highlights. Neuropeptides36, 62–71 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Darcq, E. & Kieffer, B. L. Opioid receptors: drivers to addiction? Nat. Rev. Neurosci.19, 499–514 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

