piENOX2 regulates ALKBH5-mediated Itga4 m6A modification to accelerate the progression of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 40702135
- PMCID: PMC12322066
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-025-01503-3
piENOX2 regulates ALKBH5-mediated Itga4 m6A modification to accelerate the progression of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
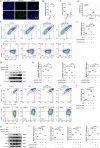
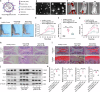
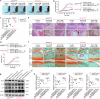
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by synovitis and presenting as symmetrical arthritis that primarily affects the small joints of the limbs. PIWI-interacting RNAs, a class of small noncoding RNAs, have garnered significant attention due to their critical involvement in various pathological conditions, including reproductive diseases, cancers and other disorders. Here we observe elevated levels of macrophage-derived piENOX2 in the synovial tissues of both patients with RA and mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). It was found that transfection with a piENOX2 mimic promoted M1 macrophage polarization, while a piENOX2 inhibitor facilitated M2 polarization. In vivo, a piENOX2 inhibitor significantly alleviated disease progression, reduced systemic inflammation and preserved the integrity of articular cartilage in CIA mice. Mechanistic analyses indicated that the piENOX2 effects were due to its targeting Alkbh5 mRNA for degradation. In a Alkbh5 conditional-knockout mouse model of CIA, the therapeutic effects of a piENOX2 inhibitor, including inflammation suppression and cartilage protection, were reduced compared with control mice. A comprehensive analyses using methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing and methylated RNA immunoprecipitation and quantitative PCR revealed that piENOX2 regulated ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of Itga4 mRNA, thereby influencing macrophage polarization through the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. These findings provide important insights into the complex roles of PIWI-interacting RNAs in RA progression and indicate potential avenues for therapeutic intervention.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Smith, M. H. & Berman, J. R. What is rheumatoid arthritis? Jama327, 1194 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Smolen, J. S. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis.82, 3–18 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Aravin, A. et al. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature442, 203–207 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Girard, A., Sachidanandam, R., Hannon, G. J. & Carmell, M. A. A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature442, 199–202 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2024M752135/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2023M732376/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 82302031/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- ZR2024QH033/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

