Structural variation in 1,019 diverse humans based on long-read sequencing
- PMID: 40702182
- PMCID: PMC12350158
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09290-7
Structural variation in 1,019 diverse humans based on long-read sequencing
Abstract
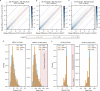
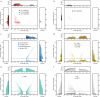
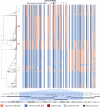
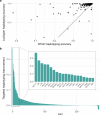
Genomic structural variants (SVs) contribute substantially to genetic diversity and human diseases1-4, yet remain under-characterized in population-scale cohorts5. Here we conducted long-read sequencing6 in 1,019 humans to construct an intermediate-coverage resource covering 26 populations from the 1000 Genomes Project. Integrating linear and graph genome-based analyses, we uncover over 100,000 sequence-resolved biallelic SVs and we genotype 300,000 multiallelic variable number of tandem repeats7, advancing SV characterization over short-read-based population-scale surveys3,4. We characterize deletions, duplications, insertions and inversions in distinct populations. Long interspersed nuclear element-1 (L1) and SINE-VNTR-Alu (SVA) retrotransposition activities mediate the transduction8,9 of unique sequence stretches in 5' or 3', depending on source mobile element class and locus. SV breakpoint analyses point to a spectrum of homology-mediated processes contributing to SV formation and recurrent deletion events. Our open-access resource underscores the value of long-read sequencing in advancing SV characterization and enables guiding variant prioritization in patient genomes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Z.D., J.N.J. and N.P. are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG. J.S. is an employee of BI X GmbH. E.B. is a consultant for and shareholder of Oxford Nanopore Technologies. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Update of
-
Long-read sequencing and structural variant characterization in 1,019 samples from the 1000 Genomes Project.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 20:2024.04.18.590093. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.18.590093. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nature. 2025 Aug;644(8076):442-452. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09290-7. PMID: 38659906 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Spielmann, M., Lupiáñez, D. G. & Mundlos, S. Structural variation in the 3D genome. Nat. Rev. Genet.19, 453–467 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Weischenfeldt, J., Symmons, O., Spitz, F. & Korbel, J. O. Phenotypic impact of genomic structural variation: insights from and for human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet.14, 125–138 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

