Complex genetic variation in nearly complete human genomes
- PMID: 40702183
- PMCID: PMC12350169
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09140-6
Complex genetic variation in nearly complete human genomes
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Complex genetic variation in nearly complete human genomes.Nature. 2025 Sep;645(8081):E6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09547-1. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40858940 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
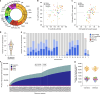
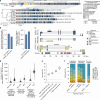
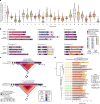
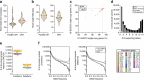
Diverse sets of complete human genomes are required to construct a pangenome reference and to understand the extent of complex structural variation. Here we sequence 65 diverse human genomes and build 130 haplotype-resolved assemblies (median continuity of 130 Mb), closing 92% of all previous assembly gaps1,2 and reaching telomere-to-telomere status for 39% of the chromosomes. We highlight complete sequence continuity of complex loci, including the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), SMN1/SMN2, NBPF8 and AMY1/AMY2, and fully resolve 1,852 complex structural variants. In addition, we completely assemble and validate 1,246 human centromeres. We find up to 30-fold variation in α-satellite higher-order repeat array length and characterize the pattern of mobile element insertions into α-satellite higher-order repeat arrays. Although most centromeres predict a single site of kinetochore attachment, epigenetic analysis suggests the presence of two hypomethylated regions for 7% of centromeres. Combining our data with the draft pangenome reference1 significantly enhances genotyping accuracy from short-read data, enabling whole-genome inference3 to a median quality value of 45. Using this approach, 26,115 structural variants per individual are detected, substantially increasing the number of structural variants now amenable to downstream disease association studies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: E.E.E. is a scientific advisory board member of Variant Bio. C. Lee is a scientific advisory board member of Nabsys. S.K. has received travel funds to speak at events hosted by ONT. J.O.K., T.M. and D.P. have previously disclosed a patent application (no. EP19169090) relevant to Strand-seq. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Complex genetic variation in nearly complete human genomes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 25:2024.09.24.614721. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.24.614721. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nature. 2025 Aug;644(8076):430-441. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09140-6. PMID: 39372794 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 CA259309/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM138212/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM133600/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG011649/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA261934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG013748/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG012798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG007497/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002385/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM139769/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010169/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM147352/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI090905/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

