Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Enhanced Myogenic Differentiation for Aligned Topography-Induced Skeletal Muscle Engineering
- PMID: 40702863
- PMCID: PMC12410905
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.202504992
Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Enhanced Myogenic Differentiation for Aligned Topography-Induced Skeletal Muscle Engineering
Abstract
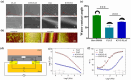
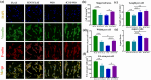
Skeletal muscle engineering utilizing bio-activators and myogenic cells to regenerate tissues for volumetric muscle loss offers a promising alternative to tissue grafts. Modified biointerfaces with aligned micro-scale topography and electroconductivity are critical for directing cellular behavior toward functional muscle constructs. This study modified polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) with aligned surface topography and functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (fCNTs), creating a conductive scaffold (0.11 µScm-1 vs original 0.51 nScm-1) with regulated hydrophilicity (76 ± 2° vs original 50 ± 10° in water contact angle) and enhanced protein absorption. The fCNT-wrinkled surfaces maintained >90% cell viability while promoting aligned myotube formation. Specifically, fCNT integration with aligned topography increased myotube length from 303.74 ± 27.61 µm to 441.63 ± 10.27 µm and elevated fusion index to 40.43% ± 2.67% within three differentiation days. Immunostaining confirmed enhanced myogenic maturation through improved cell alignment and nuclei organization. These biophysical modifications synergistically accelerated myoblast differentiation while maintaining cytocompatibility by combining electrical conductivity, optimized wettability, and directional cues. The demonstrated capacity to physiologically mimic native muscle microenvironments highlights this strategy's potential for improving muscle regeneration therapies through precise control of surface-electrotopographical properties.
Keywords: coating; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; multi‐walled carbon nanotube; muscle tissue engineering; myoblasts; topography.
© 2025 The Author(s). Small published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Patrick van Rijn reports a relationship with BiomACS BV that includes equity or stocks. P.V.R. is also the co‐founder, scientific advisor, and shareholder of BiomACS BV, a biomedical‐oriented screening company. The authors declare no other competing interests. The authors declare no further conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

