Automated transformation of unstructured cardiovascular diagnostic reports into structured datasets using sequentially deployed large language models
- PMID: 40703108
- PMCID: PMC12282380
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztaf030
Automated transformation of unstructured cardiovascular diagnostic reports into structured datasets using sequentially deployed large language models
Abstract
Aims: Rich data in cardiovascular diagnostic testing are often sequestered in unstructured reports, limiting their use.
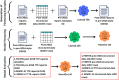
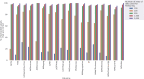
Methods and results: We sequentially deployed generative and interpretative open-source large language models (LLMs; Llama2-70b, Llama2-13b). Using Llama2-70b, we generated varying formats of transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) reports from 3000 real-world reports with paired structured elements. Using prompt-based supervised training, we fine-tuned Llama2-13b using sequentially larger batches of generated TTE reports as inputs, to extract data across 18 clinically-relevant echocardiographic fields. We evaluated the fine-tuned model, HeartDX-LM, on distinct datasets: (i) different time periods and formats at Yale New Haven Health System (YNHHS), (ii) Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC) III, and (iii) MIMIC IV. We used accuracy and Cohen's kappa as evaluation metrics and have publicly released the HeartDX-LM model. HeartDX-LM was trained on 2000 synthetic reports with varying formats and paired structured labels. We identified a lower threshold of 500 unstructured reports-structured data pairs required for fine-tuning to achieve consistent performance. At YNHHS, HeartDX-LM accurately extracted 69 144 of 70 032 values (98.7%) across 18 fields in the contemporary test set where paired structured data were available. In 100 older YNHHS reports, HeartDX-LM achieved 87.1% accuracy against expert annotations. In external validation sets from MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV, HeartDX-LM correctly extracted 615 of 707 available values (87.9%) and 201 of 220 available values (91.3%), from 100 random, expert-annotated reports from each set.
Conclusion: We developed and validated a novel approach using paired large and moderate-sized LLMs to transform free-text echocardiographic reports into tabular datasets.
Keywords: Echocardiograph; Large language models; Machine learning; Natural language processing.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: R.K. is an Associate Editor of JAMA and is a co-founder of Ensight-AI. R.K. receives support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health (under awards R01HL167858 and K23HL153775) and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation (under award 2022060). He receives support from the Blavatnik Foundation through the Blavatnik Fund for Innovation at Yale. He also receives research support, through Yale, from Bristol-Myers Squibb, BridgeBio, and Novo Nordisk. In addition to 63/346,610, R.K. is a co-inventor of U.S. Pending Patent Applications WO2023230345A1, US20220336048A1, 63/484,426, 63/508,315, 63/580,137, 63/619,241, 63/346,610, 63/562,335, and 18/813,882. R.K., E.K.O., and S.V.S. are co-inventors of the US patent application 63/606,203. R.K. and E.K.O. are co-founders of Evidence2Health, a precision health platform to improve evidence-based cardiovascular care. E.K.O. receives support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health (under award F32HL170592). He is a co-inventor of the U.S. Patent Applications 18/813,882, 17/720,068, 63/619,241, 63/177,117, 63/580,137, 63/606,203, 63/562,335, US11948230B2, and US20210374951A1. He has been a consultant for Caristo Diagnostics Ltd and Ensight-AI Inc., and has received royalty fees from technology licensed through the University of Oxford. S.V.S. works as a data scientist at Evidence2Health (outside the current work). G.N.N. is a founder of Renalytix, Pensieve, and Verici and provides consultancy services to AstraZeneca, Reata, Renalytix, and Pensieve. He also has equity in Renalytix, Pensieve, and Verici.
Figures


Update of
-
Automated Transformation of Unstructured Cardiovascular Diagnostic Reports into Structured Datasets Using Sequentially Deployed Large Language Models.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 8:2024.10.08.24315035. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.08.24315035. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2025 Apr 02;6(4):783-796. doi: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztaf030. PMID: 39417094 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Automated Transformation of Unstructured Cardiovascular Diagnostic Reports into Structured Datasets Using Sequentially Deployed Large Language Models.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 8:2024.10.08.24315035. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.08.24315035. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2025 Apr 02;6(4):783-796. doi: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztaf030. PMID: 39417094 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A dataset and benchmark for hospital course summarization with adapted large language models.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2025 Mar 1;32(3):470-479. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocae312. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2025. PMID: 39786555
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging a foundation model zoo for cell similarity search in oncological microscopy across devices.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 18;15:1480384. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1480384. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40606969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Consultant HIT. Why Unstructured Data Holds the Key to Intelligent Healthcare Systems. Atlanta (GA): HIT Consultant; 2015.
-
- Hashir M, Sawhney R. Towards unstructured mortality prediction with free-text clinical notes. J Biomed Inform 2020;108:103489. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
