Review and recommendations for using artificial intelligence in intracoronary optical coherence tomography analysis
- PMID: 40703128
- PMCID: PMC12282360
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztaf053
Review and recommendations for using artificial intelligence in intracoronary optical coherence tomography analysis
Abstract
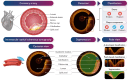
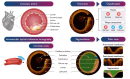
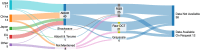
Artificial intelligence (AI) tools hold great promise for the rapid and accurate diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD) from intravascular optical coherent tomography (IVOCT) images. Numerous papers have been published describing AI-based models for different diagnostic tasks, yet it remains unclear, which models have potential clinical utility and have been properly validated. This systematic review considered published literature between January 2015 and December 2024 describing AI-based diagnosis of CAD using IVOCT. Our search identified 8600 studies, with 629 included after initial screening and 39 studies included in the final systematic review after quality screening. Our findings indicate that most of the identified models are not currently suitable for clinical use, primarily due to methodological flaws and underlying biases. To address these issues, we provide recommendations to improve model quality and research practices to enhance the development of clinically useful AI products.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Intravascular imaging; Machine learning; Optical coherance tomography.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M.B. and M.R. are founders of Octiocor Ltd., a company developing software for analysing IVOCT imaging.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence for diagnosing exudative age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 17;10(10):CD015522. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015522.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39417312
-
Artificial intelligence for detecting keratoconus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 15;11(11):CD014911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014911.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37965960 Free PMC article.
-
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) for detection of macular oedema in patients with diabetic retinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 7;1(1):CD008081. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008081.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25564068 Free PMC article.
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Research status, hotspots and perspectives of artificial intelligence applied to pain management: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02296-w. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40580377
References
-
- Sinclair H, Bourantas C, Bagnall A, Mintz GS, Kunadian V. OCT for the identification of vulnerable plaque in acute coronary syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 2015;8:198–209. - PubMed
-
- Brezinski ME, Tearney GJ, Bouma BE, Izatt JA, Hee MR, Swanson EA, et al. Optical coherence tomography for optical biopsy: properties and demonstration of vascular pathology. Circulation 1996;93:1206–1213. - PubMed
-
- Tearney GJ, Regar E, Akasaka T, Adriaenssens T, Barlis P, Bezerra HG, et al. Consensus standards for acquisition, measurement, and reporting of intravascular optical coherence tomography studies: a report from the international working group for intravascular optical coherence tomography standardization and validation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;59:1058–1072. - PubMed
-
- Shah M, Najam O, Bhindi R, De Silva K. Calcium modification techniques in complex percutaneous coronary intervention. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2021;14:E009870. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
