Global, regional, and national burden of gastroesophageal reflux disease (1990-2021): age-period-cohort analysis and Bayesian projections
- PMID: 40703162
- PMCID: PMC12283765
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1576527
Global, regional, and national burden of gastroesophageal reflux disease (1990-2021): age-period-cohort analysis and Bayesian projections
Abstract
Background: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common chronic upper gastrointestinal disorder that causes discomfort and increases the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. The global burden of GERD has steadily increased, establishing it as a critical public health issue. This study systematically evaluated the global, regional, and national burden of GERD from 1990 to 2021, revealing epidemiological trends and regional disparities to inform targeted intervention strategies.
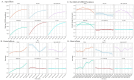
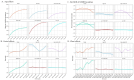
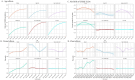
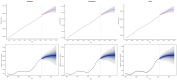
Methods: We utilized data from the 2021 Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) to assess the prevalence, incidence, and years lived with disability (YLDs) of GERD. Key indicators included age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR), age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR), age-standardized YLDs rate (ASYR), and estimated annual percentage change (EAPC). Analyses were stratified by age, gender, and socio-demographic index (SDI). Age-period-cohort (APC) models were applied to examine trends in the 15-49 age group, and Bayesian APC models were used to project future trends.
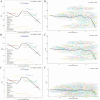
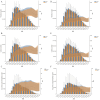
Results: In 2021, global GERD prevalence reached 825.6 million (95% uncertainty interval: 732.99-925.56 million). From 1990 to 2021, incident cases, prevalent cases, and YLDs rose by 83.16, 80.06, and 82.46%, respectively. The ASIR, ASPR, and ASYR all showed upward trends, with EAPCs of 0.097, 0.076, and 0.083. The highest burden of ASIR, ASPR, and ASYR was observed in Tropical Latin America in 2021, while the lowest was in East Asia. Regions with lower SDI had higher ASIR, ASPR, and ASYR. In the 15-49 age group, the GERD burden increased with age across all SDI regions, with unfavorable period effects observed in high and high-middle SDI regions, as well as adverse cohort effects in high-middle and middle SDI regions. Projections indicate that by 2035, global GERD cases in this age group will reach 527.2 million (ASPR: 12,082.06/100,000), with 214.6 million incident cases (ASIR: 4,916.68/100,000) and 4.1 million YLDs (ASYR: 94.47/100,000).
Conclusion: GERD poses a growing global health challenge. Insights from these observed epidemiological patterns can assist policymakers in developing targeted measures to reduce its impact, particularly in high-risk regions and younger demographics.
Keywords: Bayesian projections; GBD; age-period-cohort; age-standardized rate; gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Copyright © 2025 Mo, Liu, Cao, Gong, Wu, Lin and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The global burden of fractures and its underlying etiologies: results from and further analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Arch Osteoporos. 2025 Aug 6;20(1):111. doi: 10.1007/s11657-025-01596-3. Arch Osteoporos. 2025. PMID: 40764873
-
Global, Regional, and National Trends in the Burden of Anxiety Disorders From 1992 to 2021: An Age-Period-Cohort Analysis Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Depress Anxiety. 2025 Jul 12;2025:4178541. doi: 10.1155/da/4178541. eCollection 2025. Depress Anxiety. 2025. PMID: 40688542 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of hearing loss from 1990 to 2021: findings from the 2021 global burden of disease study.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2527367. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2527367. Epub 2025 Jul 3. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40605509 Free PMC article.
-
National and subnational burden of brain and central nervous system cancers in China and global from 1990 to 2021: results from the global burden of disease study 2021.Arch Public Health. 2025 Jul 28;83(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13690-025-01683-4. Arch Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40722045 Free PMC article.
-
Global trends of early-onset Parkinson's disease from 1990 to 2021, and projections until to 2030: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2021.Front Neurol. 2025 Aug 1;16:1589760. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1589760. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40823314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2017 Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease Collaborators . The global, regional, and national burden of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 5:561–81. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30408-X, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

