LncRNA MIR155HG suppresses cell apoptosis by activating autophagy via miR-7036b-3p/GPNMB axis and AMPK/mTOR signaling in spinal cord injury
- PMID: 40703249
- PMCID: PMC12281537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.05.013
LncRNA MIR155HG suppresses cell apoptosis by activating autophagy via miR-7036b-3p/GPNMB axis and AMPK/mTOR signaling in spinal cord injury
Abstract
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) participate in spinal cord injury (SCI) development through regulating autophagy and neuronal apoptosis. Previously, MIR155HG was identified as an upregulated lncRNA in rat bladder tissues harvested after SCI operation. Our study aimed to elucidate the function of MIR155HG in SCI.
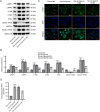
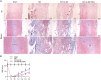
Methods: Glutamate (Glu)-stimulated primary mouse spinal cord neurons were used as SCI cellular models. Contusion-induced SCI mouse models were established using an improved weightlessness method. Neuronal apoptosis and autophagy affected by MIR155HG or GPNMB silencing were assessed by TUNEL staining, flow cytometry assay, western blotting, and immunofluorescence staining. The binding of miR-7036b-3p on MIR155HG (or GPNMB) was verified by luciferase reporter assay. Histological changes were observed through HE and Masson staining.
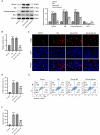
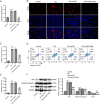
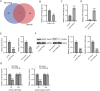
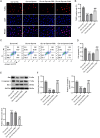
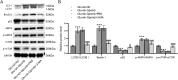
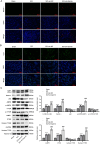
Results: MIR155HG and GPNMB expression was elevated while miR-7036b-3p expression was reduced in SCI. MIR155HG silencing attenuated the apoptosis in Glu-stimulated neurons and ameliorated glial scar formation and motor function of SCI mice. GPNMB knockdown mitigated apoptosis, enhanced autophagy, activated AMPK phosphorylation, and repressed mTOR phosphorylation. MIR155HG upregulated GPNMB expression by sponging miR-7036b-3p. The autophagy inhibitor 3-MA reversed the above changes caused by GPNMB depletion.
Conclusion: MIR155HG knockdown alleviated neuronal apoptosis by enhancing autophagy in SCI via miR-7036b-3p/GPNMB axis and AMPK/mTOR pathway.
Keywords: AMPK/mTOR; Apoptosis; Autophagy; GPNMB; MIR155HG; Spinal cord injury.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
miR-210 Regulates Autophagy Through the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Reduces Neuronal Cell Death and Inflammatory Responses, and Enhances Functional Recovery Following Cerebral Hemorrhage in Mice.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jun 5;50(3):180. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04434-7. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40471451 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking the MIR155HG/miR-155 axis reduces CTGF-induced inflammatory cytokine production and α-SMA expression via upregulating AZGP1 in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts.Cell Signal. 2024 Aug;120:111202. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111202. Epub 2024 May 9. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38729323
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 Regulates the Activation of Astrocytes Through lncRNA-Malat1/miR-124-3p/Lamc1 Axis Driving PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway, Promoting the Repair of Spinal Cord Injury.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Nov;30(11):e70103. doi: 10.1111/cns.70103. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39491316 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA XIST promotes carboplatin resistance of ovarian cancer through activating autophagy via targeting miR-506-3p/FOXP1 axis.J Gynecol Oncol. 2022 Nov;33(6):e81. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2022.33.e81. J Gynecol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36335987 Free PMC article.
-
MYCN-mediated pyroptosis and inflammation in the molecular mechanism of MicroRNA-202-3P promote functional recovery in spinal cord injury.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Aug 14;164:115349. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.115349. Online ahead of print. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40815987
References
-
- Stein D.M., Knight W.A.t. Emergency neurological Life support: traumatic spine injury. Neurocritical Care. 2017;27(Suppl 1):170–180. - PubMed
-
- Kumar R., et al. Traumatic spinal injury: global epidemiology and worldwide volume. World Neurosurg. 2018;113:e345–e363. - PubMed
-
- Li H.T., et al. Exendin-4 enhances motor function recovery via promotion of autophagy and inhibition of neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016;53(6):4073–4082. - PubMed
-
- Li J., et al. Neuroprotective effects of oxymatrine via triggering autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis following spinal cord injury in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023;60(8):4450–4471. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

