Leveraging meaning-induced neural dynamics to detect covert cognition via EEG during natural language listening-a case series
- PMID: 40703721
- PMCID: PMC12285682
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1616963
Leveraging meaning-induced neural dynamics to detect covert cognition via EEG during natural language listening-a case series
Abstract
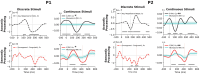
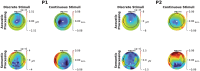
At least a quarter of adult patients with severe brain injury in a disorder of consciousness may have cognitive abilities that are hidden due to motor impairment. In this case series, we developed a tool that extracted acoustic and semantic processing biomarkers from electroencephalography recorded while participants listened to a story. We tested our method on two male adolescent survivors of severe brain injury and showed evidence of acoustic and semantic processing. Our method identifies cognitive processing while obviating demands on attention, memory, and executive function. This lays a foundation for graded assessments of cognition recovery across the spectrum of covert cognition.
Keywords: cognitive function; disorder of consciousness; natural language; pediatric; temporal response function (TRF).
Copyright © 2025 Alkhoury, O'Sullivan, Scanavini, Dou, Arora, Hamill, Patchell, Radanovic, Watson, Lalor, Schiff, Hill and Shah.
Conflict of interest statement
The new method is the subject of two submitted patent applications, and also intersects with one issued patent, by some of the authors: (i) SS, NH, EL, and NS: System and method for evaluating the brain's response to spoken language in ADRD (application submitted 2024: PCT/US2024/31951). (ii) SS, NH, EL, JO'S, and NS System and method for evaluating the brain's response to spoken language (application submitted 2022: PCT/US2022/81445; US from PCT 18/718,132; EP 22847505.9; World: WO/2023/114767). (iii) NS, C. Braiman, and C. Reichenbach: A sensory evoked diagnostic and brain-computer interface for the assessment of brain function in brain-injured patients (US Patent No. 11,759,146 issued 2023; EP3589188 issued 2024). Between initial submission and final revision of this article, authors SS, NH, EL, and NS co-founded Cognitive Signals, Inc., a company engaged in the development of technologies related to the subject matter of this manuscript. Potential conflicts of interest arising from this affiliation have been disclosed and are being managed in accordance with the policies of the authors' respective institutions. The authors declare no further conflict of interest. All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with its submission. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bialas O., Dou J., Lalor E. C. (2023). mtrfpy: A python package for temporal response function analysis. J. Open Source Softw. 8:5657. 10.21105/joss.05657 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

