Fragmentomic-based algorithm to computationally predict tumor-somatic, germline, and clonal hematopoiesis variant origin in liquid biopsy
- PMID: 40704056
- PMCID: PMC12284786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlb.2025.100311
Fragmentomic-based algorithm to computationally predict tumor-somatic, germline, and clonal hematopoiesis variant origin in liquid biopsy
Abstract
Purpose: Genomic profiling of tumors by liquid biopsy (LBx) is a pragmatic alternative to profiling tissue. Despite recent methodologic advances, clonal hematopoiesis (CH) variants arising from hematopoietic stem cells may confound LBx results. Distinguishing the origin of variants detected by LBx will greatly enhance treatment decision-making for patients with cancer.
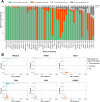
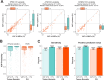
Experimental design: We sequenced DNA isolated from paired plasma and white blood cells (WBC) at equal depth to train (n = 1977) and validate (n = 658) Variant Origin Prediction (VOP), a machine learning algorithm that leverages fragmentomics to generate probabilities that a short variant (SV) detected by LBx is tumor-somatic, germline, or CH in origin. The algorithm's classifications were validated for accuracy using paired WBC DNA and for reproducibility using LBx replicates.
Results: We show that 68% of LBx detected at least one reportable variant of CH origin. Our fragmentomic-based algorithm differentiated reportable tumor and CH variants with high sensitivity, high positive predictive value (PPA >93%, PPV >91%), and high reproducibility (>94%). Critically, VOP performs well for SVs with VAFs ≤1% (PPV >90%), as well as in genes known to harbor both CH and tumor-somatic SVs, such as TP53 (PPV >88%). In a longitudinal cohort of 422 metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) cases, VOP accurately predicted baseline variant origins, and allowed separate tracking of tumor-somatic and CH variants, including newly detected variants, at subsequent timepoints.
Conclusions: VOP is a highly accurate and reproducible method to predict the origin of SVs detected in LBx without reliance on WBC sequencing. VOP can reduce inappropriate use of targeted therapies and their toxicities for patients with variants of CH origin and enables accurate tumor profiling and monitoring.
Keywords: Clonal hematopoiesis; Comprehensive genomic profiling; Fragmentomics; Germline; Monitoring; ctDNA; liquid biopsy.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: DWB, DS, ADF, SH, MM, KP, EP, AK, ML, SZ, ZK, DF, RWM, JH, LAA, AA, BY, BJD, JDH, HT, CX are employees of Foundation Medicine, a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche, and have equity interest in Roche. ZJA is an employee of Genentech, a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche, and have equity interest in Roche. 10.13039/501100017484TP serves as a consultant and receives honoraria, grants or fundings from 10.13039/100004325AstraZeneca, BMS, 10.13039/100010544Exelixis, 10.13039/100017655Incyte, 10.13039/501100014382Ipsen, 10.13039/100030732MSD, 10.13039/100004336Novartis, 10.13039/100004319Pfizer, 10.13039/100010293Seattle Genetics, 10.13039/100004334Merck Serono, Astellas, 10.13039/100004331Johnson & Johnson, 10.13039/501100003769Eisai, 10.13039/100004337Roche, Mashup. CS received research fundings from Johnson and Johnson, Pfizer, Astellas, Bayer and provided consultancy or advisory to Johnson & Johnson, Astellas, Bayer, Genentech/Roche, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Advancell, BMS. ESA reports grants and personal fees from Janssen, 10.13039/100004339Sanofi, 10.13039/100004326Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Curium, 10.13039/100019794MacroGenics, 10.13039/100004334Merck, 10.13039/100004319Pfizer, and 10.13039/100004325AstraZeneca, personal fees from AADI Biosciences, Alkido Pharma, Astellas, 10.13039/100002429Amgen, Blue Earth, Boundless Bio, Corcept Therapeutics, 10.13039/100030841Exact Sciences, 10.13039/100019714Foundation Medicine, Hookipa Pharma, 10.13039/100020388Invitae, 10.13039/100004312Eli Lilly and Company, 10.13039/100016273Menarini Silicon Biosystems, Tango Therapeutics, 10.13039/100022884Tempus, and Z-Alpha, and grants from 10.13039/100004336Novartis, 10.13039/100006436Celgene, and 10.13039/501100024580Orion outside the submitted work; and a patent for an AR-V7 biomarker technology issued and licensed to Qiagen. DG reports grants from 10.13039/100002429Amgen, 10.13039/100013870Astex Pharma, and 10.13039/100004328Genentech, serves as a consultant for 10.13039/100004325AstraZeneca, 10.13039/100030841Exact Sciences, 10.13039/100004328Genentech, Guardant 10.13039/100018696Health, IO Biotech, OncoHost, Adagene, Henlius USA, 10.13039/100019714Foundation Medicine, One-carbon Therapeutics, and 10.13039/100004339Sanofi, and serves on the Advisory Board for 10.13039/100020582AbbVie Foundation, Janssen, 10.13039/100004334Merck & Co, 10.13039/100016957Mirati Therapeutics, 10.13039/100009857Regeneron, and Revolution Medicine. Given his role as Editorial Board Member, DG had no involvement in the peer-review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer review. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

