Characterization of the aroma variances of duck broth from different part by HS-SPME-GC-MS, HS-GC-IMS and sensory evaluation
- PMID: 40704181
- PMCID: PMC12284783
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102789
Characterization of the aroma variances of duck broth from different part by HS-SPME-GC-MS, HS-GC-IMS and sensory evaluation
Abstract
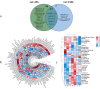
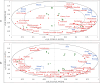
China is the world's largest producer of meat ducks. Decoding the aroma composition of duck broth (DB) produced from different parts can help improve the sensory quality and diversified development of duck meat products. The aroma compounds of DB stewed from seven parts were characterized by solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry, sensory evaluation, odor activity value (OAV) analysis, and partial least squares regression (PLSR) analysis. Two categories including the DB produced from head part and DB produced from the rest of the six parts were divided based on the hierarchical cluster analysis of pleasant (meaty, fatty, savory, and roasted) and unpleasant (bloody, mutton, animal and sour) aroma attributes. A total of 113 aroma compounds were identified, among which aldehydes, alcohols and the nitrogen-containing compound (mainly trimethylamine) were the most abundant. Significant variances were observed among the seven DB samples. The highest total concentration of volatile compounds was observed in from duck leg broth (2924.2 μg/L) and the lowest was duck wing broth (1935.96 μg/L). Thirty aroma compounds with OAVs ≥ 1 in DB were confirmed. Twenty compounds were predicted as the potential compounds contributing to aroma profile differences among seven DBs by PSLR analysis. Considering their higher OAVs and coefficient, hexanal, octanal, nonanal, (E)-2-nonenal, ethyl isovalerate, dimethyl sulfide, and trimethylamine were identified as the differential markers of DBs.
Keywords: Aroma compounds; Duck broth; Gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry; Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; Sensory evaluation.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Analysis of volatile aroma components in tobacco by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry coupled with headspace solid phase microextraction].Se Pu. 2025 Jul;43(7):793-804. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.10004. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 40610773 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Identification of volatile flavor substances in four key muscle portions of five Tibetan sheep breeds.J Sci Food Agric. 2025 Aug 30;105(11):5950-5961. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.14319. Epub 2025 May 1. J Sci Food Agric. 2025. PMID: 40312977
-
Aroma-Driven Differentiation of Wuyi Shuixian Tea Grades: The Pivotal Role of Linalool Revealed by OAV and Multivariate Analysis.Foods. 2025 Jun 21;14(13):2169. doi: 10.3390/foods14132169. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40646921 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
-
- An Y., Wen L., Li W., Zhang X., Hu Y., Xiong S. Characterization of warmed-over flavor compounds in surimi gel made from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry, aroma extract dilution analysis, aroma recombination, and omission studies. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2022;70(30):9451–9462. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

