Serum Lactate Levels and Their Correlation With Hospital Outcomes in ICU Patients With Shock: A Cross-Sectional Study at a Tertiary Care Center
- PMID: 40704246
- PMCID: PMC12284338
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.86564
Serum Lactate Levels and Their Correlation With Hospital Outcomes in ICU Patients With Shock: A Cross-Sectional Study at a Tertiary Care Center
Abstract
Background and aim: Shock is a life-threatening state characterized by inadequate tissue perfusion to meet metabolic demand, leading to organ failure and death. Serum lactate, a byproduct of anaerobic metabolism, has been identified as a significant biomarker for assessing shock severity and predicting outcomes. This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between serial serum lactate levels and hospital outcomes in patients with shock admitted to the ICU at Manik Hospital.
Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted, including 124 adult patients diagnosed with shock and admitted to the ICU between April 2023 and December 2023. Serum lactate levels were measured at admission and 24 hours later. Outcomes assessed included mortality, mechanical ventilation, ICU stay duration, and shock index. Data were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics, including Pearson correlation and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
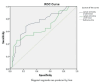
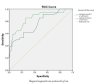
Results: The study participants had a mean age of 50.7 years, with hypovolemic shock being the most common condition, affecting 61.3% (n=76). A moderate positive correlation was found between serum lactate levels and the shock index at both admission (r=0.273) and 24 hours (r=0.293) (p<0.001). Elevated lactate levels at both time points were significantly associated with increased mortality and the need for mechanical ventilation (p<0.001). At admission, lactate predicted mortality with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.765, which increased to 0.848 at 24 hours. Lactate also showed good predictive power for the need for mechanical ventilation, with AUC values of 0.737 at admission and 0.664 at 24 hours.
Conclusions: Elevated serum lactate levels, both at admission and 24 hours, were identified as strong predictors of mortality, mechanical ventilation, and prolonged ICU stay in shock patients. Serial lactate measurements were found to provide valuable prognostic information, aiding in early risk stratification and personalized patient management. Further research was recommended to validate these findings across multiple centers and explore the role of lactate clearance in predicting recovery.
Keywords: cardiogenic shock; hospital outcomes; intensive care unit (icu); septic shock; serum lactate; shock; shock index; tertiary care center.
Copyright © 2025, Baser et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Seth Nandlal Dhoot Hospital Institutional Ethics Committee issued approval #631. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Serum Ferritin Levels as a Prognostic Marker for Predicting Outcomes in Children With Severe Sepsis and Their Correlation With Pediatric Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score.Cureus. 2025 May 19;17(5):e84436. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84436. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40539133 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum lactate and mortality in critically ill ischemic stroke patients based on MIMIC-IV data.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 18;15(1):26155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11461-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40681728 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
References
-
- Koya HH, Paul M. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Shock.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
