Outbreak of melioidosis in a highly urbanized area
- PMID: 40704419
- PMCID: PMC12340941
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2539194
Outbreak of melioidosis in a highly urbanized area
Abstract
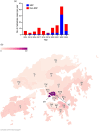
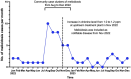
In 2022, an outbreak of melioidosis occurred at a highly urbanized district (the SSP district) in Hong Kong. There was a 5-fold increase in cases compared to the average number of cases in the preceding years, with the SSP district accounting for 71.1% of the cases. A total of 568 environmental specimens were collected, including 290 environmental samples and 38 air samples from the freshwater service reservoirs (FWSRs), 16 water samples, and 224 environmental samples from the households of infected cases. Burkholderia pseudomallei was cultured from 24 (10.7%) soil samples obtained from the lawn overlying the FWSRs supplying the SSP district or from the surroundings of the air vents used for pressure equalization in the FWSRs. These culture isolates from soil have the same genotype ST-1996 as the patients' isolates. As B. pseudomallei DNA was also detected from the swabs collected from the internal roofs of the FWSRs and inside the water tap at the home of an infected case, the chlorine concentration at the upstream treatment plant outlet was increased from 1 to 1.2 ppm as a precautionary measure. The number and proportion of newly diagnosed melioidosis cases from the SSP district significantly reduced from 32 (71.1%) in 2022 to 6 (35.3%) in 2023 (p = 0.018).
Keywords: Burkholderia pseudomallei; Melioidosis; outbreak; water; water chlorination.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
