ADAR1 mRNA quantification for predicting HSIL in persons with HIV and abnormal anal cytology
- PMID: 40704972
- PMCID: PMC12407038
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.70050
ADAR1 mRNA quantification for predicting HSIL in persons with HIV and abnormal anal cytology
Abstract
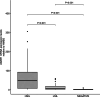
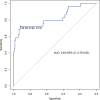
Anal squamous cell carcinoma is a significant concern among people with HIV (PWH), with high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) as its precursor. Current screening, primarily based on abnormal anal cytology, often results in unnecessary high-resolution anoscopies (HRA) due to limited specificity. This study evaluates whether quantifying Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA-1 (ADAR1) mRNA in anal swabs improves HSIL prediction and optimizes HRA selection. In this prospective cohort, HIV-positive adults with abnormal anal cytology underwent HRA. ADAR1 mRNA levels were quantified from anal swabs, and human papillomavirus (HPV) genotyping was performed. The diagnostic performance of ADAR1 mRNA was assessed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and compared with E6/E7 mRNA detection for high-risk HPV (HR-HPV). HSIL was confirmed by biopsy in 40 of 171 participants (23.4%). HSIL cases had significantly higher ADAR1 mRNA levels (median: 49.4 vs. 4.1 relative units [RU], p < .001) and a greater median number of HPV genotypes (5 vs. 3, p < .001). ROC analysis for ADAR1 mRNA yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.83 (95% CI: 0.75-0.92). At a cut-off of ≥24.8 RU, it demonstrated 73% sensitivity, 92% specificity, 74% positive predictive value, and 92% negative predictive value. Compared to E6/E7 mRNA, ADAR1 mRNA improved screening accuracy (64%-88%) and reduced HRA referrals (77.2%-48.8%). ADAR1 mRNA quantification reliably predicts HSIL in PWH with abnormal anal cytology. Integrating ADAR1 mRNA measurement into anal cancer screening protocols may enhance diagnostic accuracy, reduce unnecessary invasive procedures, and alleviate the burden on limited HRA resources.
Keywords: ADAR1; HPV; alternative prediction method; anal HSIL.
© 2025 The Author(s). International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

