Identifying genetic variations in emm 89 Streptococcus pyogenes associated with severe invasive infections
- PMID: 40704999
- PMCID: PMC12289306
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.101938
Identifying genetic variations in emm 89 Streptococcus pyogenes associated with severe invasive infections
Abstract
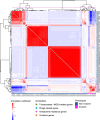
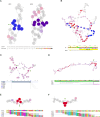
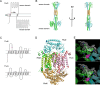
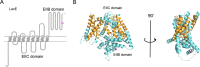
Streptococcus pyogenes causes mild human infections as well as life-threatening invasive diseases. Since the mutations known to enhance virulence to date account for only half of the severe invasive infections, additional mechanisms/mutations need to be identified. Here, we conducted a genome-wide association study of emm89 S. pyogenes strains to comprehensively identify pathology-related bacterial genetic factors (single-nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs], indels, genes, or k-mers). Japanese (n = 311) and global (n = 666) cohort studies of strains isolated from invasive or non-invasive infections revealed 17 and 1075 SNPs/indels and 2 and 169 genes, respectively, that displayed associations with invasiveness. We validated one of them, a non-invasiveness-related point mutation, fhuB T218C, by structure predictions and introducing it into a severe invasive strain and confirmed that the mutant showed slower growth in human blood. Thus, we report novel mechanisms that convert emm89 S. pyogenes to an invasive phenotype and a platform for establishing novel treatments and prevention strategies.
Keywords: S. pyogenes; Streptococcus pyogenes; ferric iron transporter; infectious disease; invasive infections; microbiology; pangenome analysis; pangenome-wide association study.
© 2025, Ono et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MO, MY, DM, YH, KH, TS, TM, RO, TY, RK, HO, NN, YK, CN, RY, HS, YM, TI, SK No competing interests declared
Figures
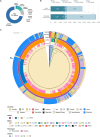


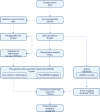
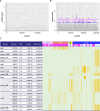

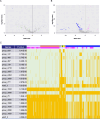

Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2024.07.02.601674
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.101938.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.101938.2
References
-
- Beall B, Facklam RR, Elliott JA, Franklin AR, Hoenes T, Jackson D, Laclaire L, Thompson T, Viswanathan R. Streptococcal emm types associated with T-agglutination types and the use of conserved emm gene restriction fragment patterns for subtyping group A streptococci. Journal of Medical Microbiology. 1998;47:893–898. doi: 10.1099/00222615-47-10-893. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berbel D, Càmara J, González-Díaz A, Cubero M, López de Egea G, Martí S, Tubau F, Domínguez MA, Ardanuy C. Deciphering mobile genetic elements disseminating macrolide resistance in Streptococcus pyogenes over a 21 year period in Barcelona, Spain. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2021;76:1991–2003. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab130. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beres SB, Kachroo P, Nasser W, Olsen RJ, Zhu L, Flores AR, de la Riva I, Paez-Mayorga J, Jimenez FE, Cantu C, Vuopio J, Jalava J, Kristinsson KG, Gottfredsson M, Corander J, Fittipaldi N, Di Luca MC, Petrelli D, Vitali LA, Raiford A, Jenkins L, Musser JM. Transcriptome remodeling contributes to epidemic disease caused by the human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes. mBio. 2016;7:e0403. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00403-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 20KK0210/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 22H03262/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 22K19618/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 22K19619/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 23H03073/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 23K19687/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 24K19854/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 2022B05/Joint Research Program of the Research Center for GLOBAL and LOCAL Infectious Diseases, Oita University
- 2025B01/Joint Research Program of the Research Center for GLOBAL and LOCAL Infectious Diseases, Oita University
- 2025B13/Joint Research Program of the Research Center for GLOBAL and LOCAL Infectious Diseases, Oita University
- JPMJSP2138/Japan Science and Technology Agency SPRING
- JP17fk0108044/AMED
- JP20fk0108130/AMED
- JP20wm0325001/AMED
- JP243fa727001h/AMED
- EX22701/Joint Usage/Research Center for Interdisciplinary Large-scale Information Infrastructures (JHPCN)
- jh230035/Joint Usage/Research Center for Interdisciplinary Large-scale Information Infrastructures (JHPCN)
- jh240003/Joint Usage/Research Center for Interdisciplinary Large-scale Information Infrastructures (JHPCN)
- jh250016/Joint Usage/Research Center for Interdisciplinary Large-scale Information Infrastructures (JHPCN)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

