Defining Lifetime Risk Thresholds for Breast Cancer Surgical Prevention
- PMID: 40705362
- PMCID: PMC12290908
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2025.2203
Defining Lifetime Risk Thresholds for Breast Cancer Surgical Prevention
Abstract
Importance: Expanding access to genetic testing and availability of validated breast cancer (BC) risk prediction models are increasingly identifying women at elevated BC risk who do not carry high-penetrance BRCA1/BRCA2/PALB2 pathogenic variants. The precise BC risk threshold for offering risk-reducing mastectomy (RRM) for BC prevention is unknown.
Objective: To define the lifetime BC risk thresholds for RRM to be cost-effective compared with nonsurgical alternatives for BC prevention.
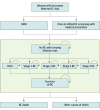
Design, setting, and participants: This economic evaluation used a decision-analytic Markov model to compare the cost-effectiveness of RRM with BC screening and medical prevention in a simulated cohort. Extensive sensitivity analyses were performed. The study setting was from a UK payer perspective over a lifetime horizon until age 80 years. The simulated cohort included women aged 30 to 60 years at varying lifetime BC risks from 17% to 50%. The study was conducted between September 2022 and September 2024.
Exposures: Undergoing RRM or receiving risk-stratified BC screening with medical prevention (tamoxifen or anastrozole).
Main outcomes and measures: The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated as incremental cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained and compared with the UK willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of £20 000 (US $27 037) to £30 000 (US $40 555) per QALY. BC cases prevented were estimated at the population level.
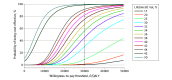
Results: In the simulated cohort of 100 000 thirty-year-old women in the UK, undergoing RRM became cost-effective at a 34% lifetime BC risk using the £30 000 (US $40 555) per QALY WTP threshold. This increased to a 42% lifetime BC risk using the £20 000 (US $27 037) per QALY WTP threshold. The identified lifetime BC risk thresholds for RRM to be cost-effective among women aged 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 years were 31%, 29%, 29%, 32%, 36%, and 42%, respectively, using the £30 000 (US $40 555) per QALY WTP threshold. Overall, undergoing RRM was deemed cost-effective for women aged 30 to 55 years with a lifetime BC risk of at least 35%, with more than 50% of simulations being cost-effective in probabilistic sensitivity analysis. Offering RRM for women with a lifetime BC risk of 35% or higher could potentially prevent approximately 6538 (95% CI, 4454-7041), or approximately 11% (95% CI, 8%-12%), of the 58 756 BC cases occurring annually in women in the UK. In the probabilistic sensitivity analysis, 20.71% to 59.96%, 44.04% to 81.29%, and 97.26% to 99.35% of simulations were cost-effective for women with 35%, 40%, and 50% lifetime BC-risk undergoing RRM at age 30 under the £20 000 to £30 000 per QALY WTP threshold, respectively.
Conclusions and relevance: In this economic evaluation, undergoing RRM appears cost-effective for women aged 30 to 55 years with a lifetime BC risk of 35% or higher. These results could have significant clinical implications to expand access to RRM beyond BRCA1/BRCA2/PALB2 pathogenic variant carriers. Future studies evaluating the acceptability, uptake, and long-term outcomes of RRM among these women are warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

