Phase separation of a PKA type I regulatory subunit regulates β-cell function through cAMP compartmentalization
- PMID: 40705714
- PMCID: PMC12289088
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003262
Phase separation of a PKA type I regulatory subunit regulates β-cell function through cAMP compartmentalization
Abstract
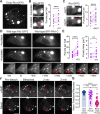
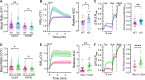
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), a ubiquitous second messenger, regulates a variety of cellular functions with high specificity. We previously showed that the type I regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), RIα, undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) to facilitate spatial compartmentalization of cAMP. However, how RIα LLPS regulates cellular function is largely unknown. Here, we identify the formation of RIα condensates in MIN6 β cells and reveal key roles for RIα LLPS in regulating β cell function. By combining CRISPR-based RIα knockout with an RIα mutant (Y122A) that exhibits defective cAMP-induced LLPS, we demonstrate that RIα LLPS drives cAMP compartmentalization to tune β cell Ca2+ and cAMP oscillation frequency, control insulin secretion, regulate CREB-mediated gene expression and prevent uncontrolled proliferation. Our data establish the Y122A mutant as a selective molecular tool for studying RIα LLPS and expand our understanding of the functional impact of LLPS-driven protein assemblies.
Copyright: © 2025 Lee et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

