Comprehensive characterization of the competitive endogenous RNA network revealing its immune-related functions in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 40705804
- PMCID: PMC12289005
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327101
Comprehensive characterization of the competitive endogenous RNA network revealing its immune-related functions in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
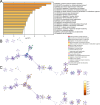
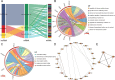
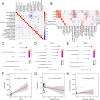
Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI) is a common complication in liver surgery and transplantation. Recent studies have revealed the significant role of the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network in HIRI. Herein, we comprehensively analyzed the HIRI-related ceRNA network and its correlation with immune-related pathways and immune cells in HIRI patients. We identified 449 lncRNAs, 26 miRNAs, and 548 mRNAs differentially expressed in HIRI patients. We constructed a HIRI-related ceRNA network in liver transplant patients consisting of 3 lncRNAs, 3 miRNAs, and 29 mRNAs. Biological function analysis showed that the HIRI-related ceRNA network contributes to HIRI progression by regulating calcium ion-related regulatory pathways and processes. An immune-related ceRNA subnetwork, which consists of 1 lncRNA (PARD6G-AS1), 1 miRNA (hsa-miRNA-125b-5p), and 4 mRNAs (PLAU, CCR5, FGF5 and IL24) was obtained. The immune-related ceRNA subnetwork was significantly related to the immune-related pathways and immune cell infiltration. The PARD6G-AS1/miR-125b-5p/IL24 axis was identified as a potential ceRNA sponge that may influence NK cell activity in HIRI. Our results underlined that the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network can positively or negatively regulate immune-related functions and infiltrating immune cells mediated HIRI, which could provide further insight into novel molecular therapeutic targets.
Copyright: © 2025 Liu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

