Physiological effects of Solanum rostratum Dunal extract and cadmium chloride complex stress on rye seedlings under freeze-thaw conditions
- PMID: 40707899
- PMCID: PMC12288345
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-07001-y
Physiological effects of Solanum rostratum Dunal extract and cadmium chloride complex stress on rye seedlings under freeze-thaw conditions
Abstract
Background: Affected by global warming, freeze-thaw occurs more frequently in Northeast China. Meanwhile, as a major grain-producing area, this region is influenced by the invasive plant Solanum rostratum Dunal. Moreover, due to the long-term application of chemical fertilizers, soil cadmium pollution has been aggravated. Therefore, crops in Northeast China may suffer from compound stress simultaneously. However, the impact of combined stress on plants has not been given enough attention, and the interrelationships between different stresses have not been thoroughly studied. This experiment adopted the indoor simulation method. By determining the changing trends and amplitudes of relative conductivity (RC), soluble protein (SP), chlorophyll (Chl), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD), the influence effects of the combined stress of freeze-thaw, S. rostratum extract, and cadmium chloride on the growth and metabolism of seedlings could be judged.
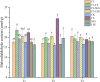
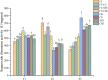
Results: Under the combined stress of freeze-thaw, cadmium chloride, and S. rostratum extract, the growth of rye seedlings was inhibited; The relative conductivity (RC) increased by 1.92-71.07%, and the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) increased by 17.34-28.11%; The soluble protein (SP) content decreased by 17.82-22.14%; The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) both increased, but POD activity was inhibited at the lowest point of freeze-thaw (-5℃); The chlorophyll (Chl) content decreased by 9.68-19.67%.
Conclusion: Stress affects osmotic pressure, and seedlings need to accumulate osmoregulatory substances to maintain cell osmotic balance. Compared to a single stress factor, the combined stress of freeze-thaw, cadmium chloride, and S. rostratum extract further enhanced the physiological damage to plants. This compound stress leads to electrolyte leakage, intensified membrane lipid peroxidation, inhibition of protein synthesis, increased osmotic pressure, and disruption of cell osmotic balance. Combined stress further promotes the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the seedlings, leading to oxidative damage and inhibiting photosynthesis.
Keywords: Allelopathy; Cadmium stress; Combined stresses; Freeze-thaw; Invasive plant; Plant physiology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: S. rostratum was collected from public land. S. rostratum is an invasive alien plant certified in the “CATALOGUE OF QUARANTINE PESTS FOR IMPORT PLANTS TO THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA”, there are no regulations restricting its collection, the collection process is permitted. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Yang L, Huang HJ, Saeed M, Huang ZF, Jiang CL, Zhang CX, Khan MI, Khan I, Wei SH. Anatomical study of seed and fruit morphology of an invasive weed buffalobur (Solanum Rostratum Dunal). Pak J Bot. 2019;51(1):241–6.
-
- Lin Y, Tan DY. The potential and exotic invasive plant:: Solanum rostratum. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica. 2007;45(5):675–85.
-
- Kalisz S, Kivlin SN, Bialic-Murphy L. Allelopathy is pervasive in invasive plants. Biol Invasions. 2021;23(2):367–71.
-
- Li FY, Fan ZP, Xiao PF, Oh K, Ma XP, Hou W. Contamination, chemical speciation and vertical distribution of heavy metals in soils of an old and large industrial zone in Northeast China. Environ Geol. 2009;57(8):1815–23.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32371777/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32371777/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32371777/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32371777/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32371777/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32371777/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20250203129SF/Key Projects of Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province
- 20250203129SF/Key Projects of Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province
- 20250203129SF/Key Projects of Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province
- 20250203129SF/Key Projects of Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province
- 20250203129SF/Key Projects of Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province
- 20250203129SF/Key Projects of Science and Technology Development Plan of Jilin Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

