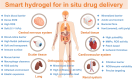
Smart hydrogels for in situ tissue drug delivery
- PMID: 40707966
- PMCID: PMC12291384
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-025-01166-2
Smart hydrogels for in situ tissue drug delivery
Abstract
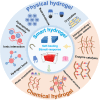
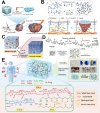
The application of smart hydrogels has become a booming research frontier in biomedical engineering. With the development of intelligent drug delivery systems, various biomimetic and biodegradable hydrogels are employed for localized drug delivery to tissues in the preclinical applications. These advanced materials are designed to match the diverse environmental and functional requirements of various tissue types and organs. This article discusses the attractive characteristics of smart hydrogels as delivery systems and reviews the design of a range of smart hydrogels, as well as the challenges of tissue-specific drug delivery, focusing on the last 5 years of frontward research.
Keywords: Controlled release; Drug delivery; Hydrogels; Smart hydrogels.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Current state of knowledge on intelligent-response biological and other macromolecular hydrogels in biomedical engineering: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Feb 1;227:472-492. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.148. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36549612
-
Stimuli-responsive peptide hydrogels for biomedical applications.J Mater Chem B. 2024 Feb 14;12(7):1748-1774. doi: 10.1039/d3tb02610h. J Mater Chem B. 2024. PMID: 38305498 Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-triggered self-assembling peptides for biomedical applications.J Mater Chem B. 2025 Jul 16;13(28):8298-8334. doi: 10.1039/d5tb00625b. J Mater Chem B. 2025. PMID: 40553109 Review.
-
Synthesis and swelling studies of modified chitosan smart hydrogels containing alkyl sulfonate anionic pendant groups as microparticles for insulin release.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 18;15(1):26166. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06494-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40681556 Free PMC article.
-
Stimuli-Responsive DNA Hydrogel Design Strategies for Biomedical Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 4;15(6):355. doi: 10.3390/bios15060355. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40558437 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li Z, Zhou Y, Li T, Zhang J, Tian H. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels: fabrication and biomedical applications. View. 2022;3(2):20200112.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

