Genetic variants in the vitamin D pathway genes are predictors of the risk of diabetic kidney disease in Central Asian Kazakhstani cohort with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 40708646
- PMCID: PMC12286948
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1630725
Genetic variants in the vitamin D pathway genes are predictors of the risk of diabetic kidney disease in Central Asian Kazakhstani cohort with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a common microvascular complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Given vitamin D's roles in glucose metabolism and renal function, this study investigated associations between common variants in vitamin D pathway genes (CYP27A1, CYP2R1, GC) and DKD risk.
Methods: This case-control study included 170 patients with DKD, 157 patients without DKD, and 118 normoglycemic healthy controls. Four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the CYP27A1 (rs17470271), CYP2R1 (rs1074165), and GC (rs4588 and rs7041) were genotyped using real-time PCR with defined clusters.
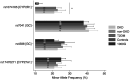
Results: The CYP27A1 rs17470271 T/T genotype was significantly associated with a reduced risk of DKD under the recessive model (AOR = 0.32, 95% CI: 0.11-0.93). A similar protective association for CYP27A1 rs17470271 T/T genotype was observed under the codominant model (OR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.12-0.99), although this did not remain statistically significant after adjustment. Likewise, the GC rs4588 T/T genotype was strongly associated with a decreased risk of DKD under the recessive (AOR = 0.30, 95% CI: 0.10-0.88) and codominant (AOR = 0.28, 95% CI: 0.09-0.85) models. However, haplotype analysis revealed contrasting findings, with the GC haplotype carrying the rs4588 G and rs7041 C alleles being associated with an increased risk of DKD compared with healthy controls.
Discussion: These findings suggest that individual variants in vitamin D pathway genes may serve as potential genetic markers for DKD risk stratification. In addition, haplotype analysis may offer complementary insight into genetic contributions to disease susceptibility.
Keywords: CYP27A1; CYP2R1; GC; diabetic nephropathy; polymorphisms; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2025 Taurbekova, Tursunov, Kabibulatova, Muxunov, Issabayeva, Atageldiyeva, Sydykova, Durmanova, Markabayeva, Starodubov, Mukhtarova, Almawi and Sarria-Santamera.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Weir MR, Agarwal R, Rossing P, Usman MS, Khan MS, Butler J, et al. Chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Arlington (VA): American Diabetes Association; (2021). 15 p.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

