Identification and validation of mitochondria-related genes in panvascular diseases
- PMID: 40708652
- PMCID: PMC12286945
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1614342
Identification and validation of mitochondria-related genes in panvascular diseases
Abstract
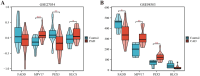
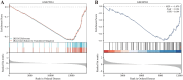
Panvascular diseases represent a spectrum of vascular conditions where atherosclerosis plays a central role in the pathophysiology. This study focused on identifying differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to mitochondria and key genes associated with peripheral artery disease (PAD) and coronary artery disease (CAD). This study identified MPV17 as a key mitochondrial gene bridging peripheral artery disease (PAD) and coronary artery disease (CAD). Analysis of GEO datasets revealed differentially expressed mitochondrial genes, with MPV17, FADD, HLCS, and PEX3 highlighted. A diagnostic nomogram, developed using LASSO and Random Forest methods, demonstrated high accuracy in predicting PAD and CAD (AUC >0.93). Furthermore, the study revealed significant alterations in immune cell infiltration associated with both diseases, suggesting a potential role for immune modulation in panvascular disease. MPV17 shows promise as a diagnostic marker for early identification and differentiation of these vascular conditions.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; immune infiltration; mitochondria-related genes; panvascular diseases; peripheral artery disease.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Ma and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Chan AW. Expanding roles of the cardiovascular specialists in panvascular disease prevention and treatment. Can J Cardiol. (2004) 20:535–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

