Two-in-one: multifunctional poloxamer hydrogel accelerates endometrial regeneration and fertility restoration through synergistic regulation of KGF-2 and NO
- PMID: 40708704
- PMCID: PMC12288958
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbaf062
Two-in-one: multifunctional poloxamer hydrogel accelerates endometrial regeneration and fertility restoration through synergistic regulation of KGF-2 and NO
Abstract
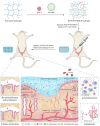
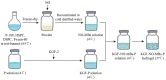
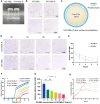
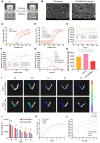
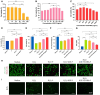
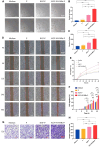
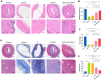
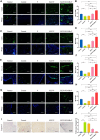
A healthy endometrium is crucial for embryo implantation and pregnancy maintenance. Thin endometrium, reduced glands and fibrosis resulting from infection or mechanical injury, are the primary causes of long-term infertility and poor pregnancy outcomes. Unfortunately, these issues have not been resolved by conventional clinical methods. Keratinocyte growth factor-2 (KGF-2) is an epithelial mitogen that regulates proliferation and migration of epithelial cells. Nitric oxide (NO) is involved in maintaining vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Poloxamer-407 (P) hydrogel is a promising topical drug delivery system due to its excellent solution-gel transition properties in response to body temperature. In this study, therapeutic NO gas was first prepared into stabilized microbubbles (NO-MBs). Subsequently, KGF-2 and NO-MBs were encapsulated into micelles of P hydrogel to form a multifunctional temperature-sensitive (28.9-31.8°C) hydrogel (KGF-NO-MBs-P hydrogel). This hydrogel not only exhibited suitable apparent viscosity, bio-adhesive and mechanical properties for application in situ but also showed sustained release of KGF-2 and NO. In vivo, KGF-NO-MBs-P hydrogel effectively restored endometrial morphology, increased the number of glands and endometrial thickness, reversed endometrial fibrosis and improved pregnancy outcomes by synergistic regulation of KGF-2 and NO. Repair of endometrial injury was closely related to promoting neovascularization, inducing endometrial cell proliferation and epithelialization, inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation and balancing collagen subtypes. Therefore, KGF-NO-MBs-P hydrogel may be useful in promoting endometrial regeneration and fertility restoration through in situ microinjection. This study represented a convenient, safe and promising method for repair of endometrial injury.
Keywords: endometrial injury; keratinocyte growth factor; nitric oxide; poloxamer hydrogel; regenerative repair.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Podocalyxin is a key negative regulator of human endometrial epithelial receptivity for embryo implantation.Hum Reprod. 2021 Apr 20;36(5):1353-1366. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deab032. Hum Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33822049 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing oral mucositis in patients with cancer receiving treatment: cytokines and growth factors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 28;11(11):CD011990. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011990.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29181845 Free PMC article.
-
Endometrial injury for pregnancy following sexual intercourse or intrauterine insemination.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 24;10(10):CD011424. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011424.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36278845 Free PMC article.
-
Endometrial injury for pregnancy following sexual intercourse or intrauterine insemination.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jun 14;(6):CD011424. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011424.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD011424. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011424.pub3. PMID: 27296541 Updated.
-
Pre-operative endometrial thinning agents before endometrial destruction for heavy menstrual bleeding.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD001124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001124. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 29;(7):CD001124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001124.pub2. PMID: 12137619 Updated.
References
-
- Zhang H, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Sheng F, Wu S, Yang F, Li W. Urinary bladder matrix scaffolds improve endometrial regeneration in a rat model of intrauterine adhesions. Biomater Sci 2020;8:988–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

