Multicenter Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial of the Romiplostim Biosimilar
- PMID: 40708707
- PMCID: PMC12288612
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.70105
Multicenter Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial of the Romiplostim Biosimilar
Abstract
Background: This was a randomized multicenter single-blinded active-controlled equivalence Phase III study evaluating the efficacy and safety of the biosimilar of romiplostim (GP40141) compared to the reference drug Nplate in patients with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
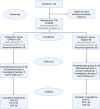
Methods: The study included 136 adult patients randomized 1:1 to receive either the biosimilar or reference drug for 26 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a platelet response (≥ 50 × 109/L) at Week 11. Key secondary endpoints included proportion of patients with durable platelet response, stable response in treatment-naive patients, incidence of bleeding, and rescue therapy usage.
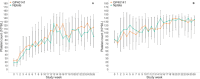
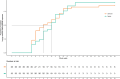
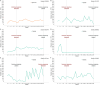
Results: The proportion of patients with platelet response after 10 weeks of therapy was 78% in the test group and 85% in the comparison group. The absolute difference in proportion between groups was -0.06 (95% CI [-0.196, 0.068] and it falls within the equivalence limits [-0.225, 0.225]). The study demonstrated equivalence in the primary endpoint, with no significant differences between the biosimilar and reference drug groups in durable responses rate, bleeding events, or safety profiles.
Conclusions: The results support the biosimilar romiplostim as an equivalent and comparable treatment option to the reference drug for patients with persistent or chronic ITP.
Trial registration: NCT06497036.
Keywords: TPO‐RA; biosimilar; primary immune thrombocytopenia; romiplostim.
© 2025 Geropharm. eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
E.A.P., V.V.K., M.L.G., V.B.S., Y.D.M., I.E.M., and R.V.D. are employees of GEROPHARM. All other authors received honoraria from GEROPHARM for participating in this study.
Figures


References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
