Safety, Efficacy, and Patient-Reported Outcomes From a Phase 2 Randomized Trial of Pozelimab and Cemdisiran Combination in Patients With Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
- PMID: 40708708
- PMCID: PMC12288694
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.70095
Safety, Efficacy, and Patient-Reported Outcomes From a Phase 2 Randomized Trial of Pozelimab and Cemdisiran Combination in Patients With Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Abstract
Introduction: Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is an ultra-rare, life-threatening disease associated with chronic intravascular hemolysis due to uncontrolled complement activation. PNH results in anemia with an increased risk of thrombosis, and often causes severe fatigue, and decreased physical function and health-related quality of life (QoL). We investigated the efficacy, safety, and patient-reported outcomes data of the combination of pozelimab (a fully human monoclonal antibody) and cemdisiran (an N-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated small interfering ribonucleic acid) from a Phase 2 trial (NCT04811716) in patients with PNH who transitioned from pozelimab monotherapy.
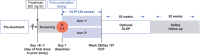
Methods: In this randomized, open-label, Phase 2 study, patients were randomized (1:1) to one of two treatment arms; both arms received subcutaneous cemdisiran 200 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) plus subcutaneous pozelimab 400 mg either Q4W (Arm 1) or every 2 weeks (Arm 2).
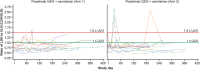
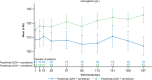
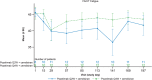
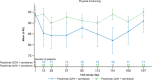
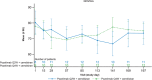
Results: Twenty-four patients were treated with combination dosing. During the 28-week open-label treatment period (OLTP), 20 patients (83.3%) maintained control of lactate dehydrogenase (≤ 1.5 × upper limit of normal) at all timepoints. The majority of patients (92%) did not require a blood transfusion. While most patients (66.7%) experienced treatment-emergent adverse events, the majority of these events were mild to moderate in severity. No meningococcal infections, thrombotic events, or deaths were reported. The combination therapy maintained improvements in patient-reported fatigue, physical functioning, and QoL throughout the OLTP.
Conclusion: Combination treatment maintained adequate hemolysis control and was generally well tolerated. Administration of pozelimab Q2W did not improve disease control as compared to pozelimab Q4W.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov/NCT04811716.
Keywords: complement; hemolysis; quality of life.
© 2025 The Author(s). eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Jun‐Ho Jang has received research funding from Alexion, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., AbbVie, Allovir, Janssen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Samsung Bioepis, and Roche Pharmaceuticals; and honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Alexion, Janssen, Samsung Bioepis, Novartis, Astella, and Vifor Pharma. Raymond Siu Ming Wong has received research funding from Amgen, Apellis, Gilead, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., AbbVie, Acerta, Bayer, Roche, UCB, and Daiichi Sankyo; and honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Apellis, Alexion, Pfizer, Spark Therapeutics, and Astella. Christopher Hartford, Rodrigo Pavani, Lisa Aurand, Quang Nguyen, Karoline Meagher, Steven Sherman, Diana Rofail, Lorah Perlee, and Amal Souttou are employees of and stockholders in Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Kosalai Mohan was an employee of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at the time the study was conducted. Richard J. Kelly has received consultancy fees/honoraria/speaker's bureau fees from Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease, Astellas, F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd, Florio, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Otsuka, and Sobi.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eculizumab for treating patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Oct 30;(10):CD010340. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010340.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25356860
-
Long-term management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis with lebrikizumab and concomitant topical corticosteroids: a 68-week randomized double-blind placebo-controlled phase III trial in Japan (ADhere-J).Br J Dermatol. 2025 Mar 18;192(4):597-610. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae394. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39442013 Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-interleukin-13 and anti-interleukin-4 agents versus placebo, anti-interleukin-5 or anti-immunoglobulin-E agents, for people with asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 19;10(10):CD012929. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012929.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34664263 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term (68 weeks) administration of nemolizumab and topical corticosteroids for prurigo nodularis in patients aged ≥ 13 years: efficacy and safety data from a phase II/III study.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jun 20;193(1):56-65. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf045. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40112876 Clinical Trial.
-
Corrector therapies (with or without potentiators) for people with cystic fibrosis with class II CFTR gene variants (most commonly F508del).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 20;11(11):CD010966. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010966.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37983082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hill A., Kelly R. J., and Hillmen P., “Thrombosis in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria,” Blood 121 (2013): 4985–4996. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
