Remdesivir Versus Sotrovimab in Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40709071
- PMCID: PMC12287540
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.71118
Remdesivir Versus Sotrovimab in Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and aim: Remdesivir and Sotrovimab have emerged as potential treatment options for patients diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This systematic review and meta-analysis sought to evaluate and compare the effectiveness and safety of these two drugs in the context of COVID-19 management.
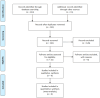
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, medRxiv, and Google Scholar up to July 2024. The effectiveness outcomes examined included mortality rate, hospitalization rate, emergency department visits, ICU admission, and adverse events. The risk of bias in nonrandomized studies of interventions was evaluated using a standardized tool, and data from the identified studies were meticulously analyzed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) software.
Results: The analysis incorporated a total of 9 studies involving 7841 patients. The meta-analysis findings indicated no significant disparity between the Remdesivir and Sotrovimab groups concerning mortality rate (odds ratio [OR] = 3.49, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.50-24.11, p = 0.20), hospitalization rate (OR = 2.11, 95% CI: 0.85-5.22, p = 0.10), emergency department visit (OR = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.11-5.62, p = 0.82), and intensive care unit (2.37, 95% CI: 0.18-29.90, p = 0.50). Moreover, comparable rates of adverse events were observed across both groups (OR = 0.98, 95% CI: 0.39-2.47, p = 0.97). The certainty of evidence for these findings was rated as low or moderate.
Conclusion: The study findings suggest that there is no significant difference in effectiveness between Remdesivir and Sotrovimab in the treatment of COVID-19 patients. Further research is needed to provide a more comprehensive comparison of these interventions for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID‐19; Remdesivir; SARS‐CoV‐2; Sotrovimab; effectiveness; safety.
© 2025 The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


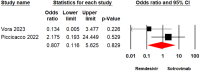


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

