Costunolide Reduces DN Inflammatory Response and Renal Thrombosis by Inhibiting NET Formation
- PMID: 40709100
- PMCID: PMC12289368
- DOI: 10.1155/jdr/1159325
Costunolide Reduces DN Inflammatory Response and Renal Thrombosis by Inhibiting NET Formation
Abstract
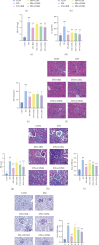
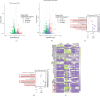
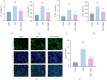
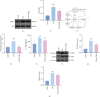
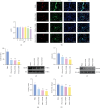
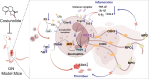
Background: Diabetic nephropathy (DN), a prevalent microvascular complication of diabetes, is characterized by chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and renal thrombosis. This study is aimed at assessing the therapeutic effects of costunolide (COS) on DN and investigating its mechanism of action in reducing inflammation and platelet activation-mediated thrombosis by inhibiting the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Methods: A DN mouse model was established using a high-sugar, high-fat diet combined with streptozotocin (STZ) administration, followed by treatment with varying doses of COS. The efficacy of COS was assessed through renal function indicators, including 24-h urinary protein levels, serum creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen, alongside renal histopathological analyses using hematoxylin-eosin, Masson's trichrome, and periodic acid-Schiff staining. Transcriptomic analysis was performed to identify gene expression changes in renal tissues after COS treatment. Based on transcriptomic findings, the impact of COS on inflammatory and platelet activation-related markers (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, CCL2, and CD41) was further evaluated. Additionally, the expression of NET formation-related factors (MPO, CitH3, IGTAM, PAD4, C3, and fibrinogen) was analyzed using immunofluorescence, western blot, and ELISA. To validate the in vivo findings, isolated neutrophils were treated with COS in vitro to assess its inhibitory effects on NET formation, including markers such as SYTOX Green, CitH3, ROS, and PAD4. Results: COS treatment significantly improved renal function and mitigated histopathological damage in DN mice. Transcriptomic analysis indicated that COS modulated pathways associated with inflammation and platelet activation, including the complement and coagulation cascades, biosynthesis of cofactors, cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions, NET formation, and NOD-like receptor signaling. COS markedly reduced the expression of inflammatory markers (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and CCL2) and the platelet activation marker CD41 in renal tissues. Moreover, COS decreased the expression of NET-related proteins, including MPO, CitH3, PAD4, IGTAM, C3, and fibrinogen, while lowering the CitH3/H3 ratio. In vitro, COS significantly inhibited PMA-induced NET formation in neutrophils, as evidenced by reduced SYTOX Green + CitH3+ expression and decreased levels of PAD4 and ROS. Conclusion: COS alleviates inflammation and platelet activation-mediated thrombosis in DN mice, potentially by inhibiting excessive NET formation. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of COS in managing DN.
Copyright © 2025 Xiangjing Wang et al. Journal of Diabetes Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

