Balancing Nutrition and Osmolality: Risk of Hyperosmolality During Individualized Fortification With Protein Fortifiers in an In Vitro Study
- PMID: 40709129
- PMCID: PMC12286768
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.86602
Balancing Nutrition and Osmolality: Risk of Hyperosmolality During Individualized Fortification With Protein Fortifiers in an In Vitro Study
Abstract
Background: Individualized fortification of human milk with protein fortifiers (PFs) and fat fortifiers (FFs) helps optimize the nutritional requirements of preterm infants but increases osmolality. This study aims to evaluate the impact of PFs and FFs on the osmolality of human milk fortified with multi-component fortifiers (MCFs).
Methods: The osmolality of 25 mL of expressed breast milk (EBM) was measured with six MCFs (1 g each), preterm formula (PTF), PF, and FF separately. Additionally, the osmolality of 25 mL of sterile water was measured with 1 g of each MCF separately. PF was added in increasing amounts (0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2 g) to fortified human milk (FHM), and the maximum amount of PF that could be added without exceeding the osmolality of 450 mOsm/kg was determined.
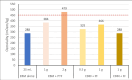
Results: The osmolality of EBM was 288 mOsm/kg, which increased to 384 mOsm/kg with the addition of 1 g of PTF. Among FHM, the highest osmolality was observed with MCF4 (428 mOsm/kg), and the lowest with MCF6 (327 mOsm/kg). The addition of 0.5 g of PF to FHM with MCF1 and MCF4 increased osmolality beyond the safe threshold but was within safe limits with MCF2, MCF3, MCF5, and MCF6. When 1 g of PF was added to FHM with MCF2 and MCF3, osmolality exceeded 450 mOsm/kg. However, osmolality remained within safe limits with the addition of 1.5 g of PF to FHM with MCF5 and MCF6. The addition of 1 g of FF did not alter the osmolality of EBM.
Conclusion: The addition of MCFs increases the osmolality of EBM, although within safe limits. However, as the addition of PF to FHM further raises the osmolality, it is essential to select the type of MCF and adjust the amount of PF to maintain osmolality within safe threshold limits.
Keywords: breastmilk fortification; human milk fortifier; hyperosmolar; lipid fortifier; multicomponent fortifier; osmolality; preterm; protein fortifier; targeted fortification.
Copyright © 2025, Basany et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Ankura Hospital Scientific Research Committee issued approval ANKURA/SRC/2024-09. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Osmolality of donor human milk rises dramatically within minutes of fortification with varied degrees depending on the fortifier used.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jun 6;13:1596255. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1596255. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40547130 Free PMC article.
-
Multicomponent fortified human milk for promoting growth in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD000343. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000343.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 08;(5):CD000343. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000343.pub3. PMID: 14973953 Updated.
-
Individualized Fortification Influences the Osmolality of Human Milk.Front Pediatr. 2018 Oct 31;6:322. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00322. eCollection 2018. Front Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30430102 Free PMC article.
-
Multicomponent fortified human milk for promoting growth in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD000343. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000343. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD000343. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000343.pub2. PMID: 10796349 Updated.
-
Clinical symptoms, signs and tests for identification of impending and current water-loss dehydration in older people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 30;2015(4):CD009647. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009647.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25924806 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
