Psychoneurological symptom clusters in patients with first stroke and relationship with inflammatory markers: a latent profile analysis
- PMID: 40709232
- PMCID: PMC12287099
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1618513
Psychoneurological symptom clusters in patients with first stroke and relationship with inflammatory markers: a latent profile analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the relationship between psychoneurological symptom clusters and inflammatory markers in patients with a first stroke.
Methods: This study investigated 227 patients with a first stroke using general information questionnaires, Numerical Rating Scale, Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Ascertain Dementia 8, Fatigue Severity Scale, and Stroke-Specific Quality of Life. Data analysis included latent profile analysis, one-way analysis of variance, and unordered multicategorical logistic analysis.
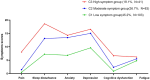
Results: The psychoneurological symptom clusters of first-stroke patients were categorized into three latent profiles: the low symptom group (45.2%), moderate symptom group (36.7%), and high symptom group (18.1%). Logistic regression analyses showed that younger age, female, higher National Institute of Health Stroke Scale score, higher interleukin-6 level, and higher hypersensitive C-reactive protein level were major predictive factors for the moderate and high symptom groups.
Conclusion: Three latent profiles of psychoneurological symptom clusters exist in patients with a first stroke and are associated with markers of inflammation (interleukin-6 and hypersensitive C-reactive protein), thereby affecting their quality of life. These findings extend previous research on psychoneurological symptom clusters in stroke. Further exploration of a broader range of inflammatory markers and psychoneurological symptom clusters is necessary to advance symptom management.
Keywords: a latent profile analysis; first stroke; inflammatory markers; psychoneurological symptom clusters; quality of life.
Copyright © 2025 Tang, Jiang, Jin, Wu and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bogosian A., Hurt C. S., Hindle J. V., McCracken L. M., Vasconcelos E Sa D. A., Axell S., et al. (2022). Acceptability and feasibility of a mindfulness intervention delivered via videoconferencing for people with Parkinson’s. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 35, 155–167. doi: 10.1177/0891988720988901, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials