This is a preprint.
BCL-2 Inhibition via Venetoclax at ART Initiation Induces Long-Term Reduction of the Intact SIV Reservoir
- PMID: 40709247
- PMCID: PMC12288516
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-7060088/v1
BCL-2 Inhibition via Venetoclax at ART Initiation Induces Long-Term Reduction of the Intact SIV Reservoir
Abstract
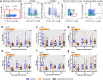
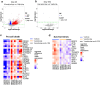
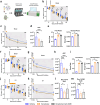
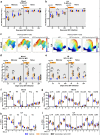
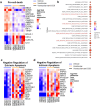
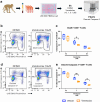
The anti-apoptotic molecule BCL-2 favors the maintenance of the CD4+ T-cell reservoir during Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection. We investigated directly in-vivo whether BCL-2 inhibition using venetoclax at the initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) would reduce the size of the viral reservoir. Twenty-four SIVmac239-infected rhesus macaques (RMs) initiated ART at day 14 post-infection (p.i.), alone or with a 10-day treatment with venetoclax or venetoclax plus CD8α depletion, and followed up to day 294 p.i. A rapid, statistically significant, and sustained reduction in the intact SIV reservoir was observed in venetoclax-treated RMs in blood and lymph nodes (LNs). This reduction was driven by reduced survival and depletion of CD4+T-cell subsets that critically contribute to the reservoir. CD4+ T-cells that persisted after venetoclax treatment exhibited elevated per-cell levels of BCL-2, reduced expression of pro-apoptotic molecules such as PUMA, increased expression of additional anti-apoptotic molecules, including BCL-xL, and a partial reduction in apoptotic sensitivity in ex vivo assays. These findings provide mechanistic insights for the venetoclax-induced pro-cell death changes in CD4+ T-cells, support the rationale for extended venetoclax dosing, and suggest that combining BCL-2 inhibition with agents targeting additional anti-apoptotic molecules can enhance clearance of the viral reservoir in HIV cure strategies.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

