Phenylalanine modulates casein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells by influencing amino acid transport and protein synthesis pathways
- PMID: 40709332
- PMCID: PMC12286789
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1598191
Phenylalanine modulates casein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells by influencing amino acid transport and protein synthesis pathways
Abstract
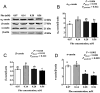
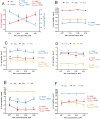
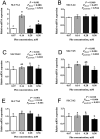
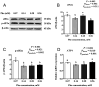
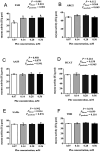
The efficiency of phenylalanine (Phe) utilization for milk protein synthesis in dairy cows is limited, and its uptake and metabolic mechanisms in the mammary tissue remaining unclear. This study investigated the effects of Phe availability (0.07, 0.14, 0.28, and 0.56 mM) on amino acid metabolism and casein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMECs) cultured for 24 h. Results showed that αS1-casein, β-casein, and κ-casein expression peaked at 0.14 mM Phe (p < 0.05). At this optimal concentration, amino acid transporters (SLC7A5, SLC7A8, and SLC38A2) were upregulated, corresponding with enhanced uptake of Met, Ile, His, and Arg (p < 0.05). The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway was activated as evidenced by increased phosphorylation of P70 S6 kinase (P70S6K) and mTOR (p < 0.05), while the general control nonderepressible 2 (GCN2) pathway was suppressed through reduced eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eIF2α) phosphorylation (p < 0.05). As Phe concentration increased, its net uptake increased linearly (Plinear < 0.05) while uptake efficiency decreased linearly (Plinear < 0.05). High Phe concentration (0.56 mM) inhibited amino acid transporter expression and reduced uptake of Leu, Pro, and Tyr (p < 0.05). Additionally, Phe-to-Tyr conversion was dynamically regulated, with phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) activity inhibited at 0.07 mM Phe (p < 0.05) but enhanced at higher concentrations, concurrent with reduced exogenous Tyr uptake (p < 0.05). These findings show that casein synthesis in BMECs is optimal at 0.14 mM Phe, coinciding with enhanced expression of amino acid transporters and activation of protein synthesis pathways. In contrast, higher Phe concentrations (0.56 mM) are associated with reduced amino acid utilization efficiency. These observations suggest potential mechanisms by which Phe concentration may regulate milk protein synthesis in dairy cows.
Keywords: amino acid metabolism; amino acid transport; bovine mammary epithelial cells; casein synthesis; mTOR signaling pathway; phenylalanine.
Copyright © 2025 Xing, Luo, Sun, Yang, Lin, Mu, Niu, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of essential amino acids availability on amino acids uptake, metabolism and casein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf079. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf079. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40084647
-
Phenylalanine Regulates Milk Protein Synthesis via LAT1-mTOR Signaling Pathways in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 6;25(23):13135. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313135. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684845 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of L-arginine and arginine-arginine dipeptide on amino acids uptake and αS1-casein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad339. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad339. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37782762 Free PMC article.
-
PTS-Related Tetrahydrobiopterin Deficiency (PTPSD).2025 Jul 10. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2025 Jul 10. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 40638773 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

