SIRT5 is associated with asthenozoospermia and regulates GC‑2 spd cell proliferation and apoptosis
- PMID: 40709377
- PMCID: PMC12332373
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13634
SIRT5 is associated with asthenozoospermia and regulates GC‑2 spd cell proliferation and apoptosis
Abstract
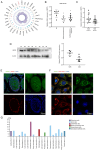
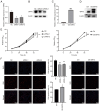
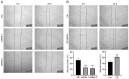
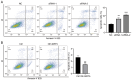
Infertility is a multifactorial condition that affects ~7% of the male population. The mechanism of male infertility primarily involves intrinsic and environmental factors, of which genetic defects are key for its occurrence. Sirtuin 5 (SIRT5) is primarily localized in mitochondria and associated with male reproduction. SIRT5 is downregulated in asthenozoospermic sperm compared with normal sperm. To explore the role of SIRT5 in male reproduction, Cell Counting Kit‑8, EdU, wound healing, and apoptosis assayswere performed in GC‑2 spd cells (mouse spermatocytes) which revealed that SIRT5 inhibited apoptosis and promoted cell proliferation and migration. Western blotting was performed and the results showed that SIRT5 was involved in the proliferation of GC‑2 spd cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. The present study demonstrated a mechanism of male infertility, which may aid in its treatment.
Keywords: GC‑2 cell; PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; asthenozoospermia; sirtuin 5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

