Role of COUP‑TFII in cardiovascular diseases and colorectal cancer: Insights into the molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance (Review)
- PMID: 40709384
- PMCID: PMC12319391
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13631
Role of COUP‑TFII in cardiovascular diseases and colorectal cancer: Insights into the molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance (Review)
Abstract
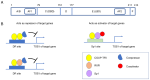
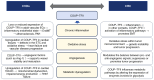
Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter‑transcription factor II (COUP‑TFII), also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group F member 2, is an orphan nuclear receptor that controls various biological processes, including development, angiogenesis, metabolism and tissue homeostasis. Structurally, COUP‑TFII comprises a DNA‑binding domain and a ligand‑binding domain, facilitating its interaction with various signaling pathways, and thereby exerting diverse biological effects. Alterations of the expression or transcriptional activity of COUP‑TFII are associated with various diseases, including cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and different types of cancer such as colorectal cancer (CRC). In the context of CVDs, COUP‑TFII serves a key role in the development and function of the vascular system. Dysregulation of COUP‑TFII leads to aberrant angiogenesis and vascular remodeling, contributing to the pathogenesis of various CVDs. In CRC, COUP‑TFII acts as either a tumor suppressor or a tumor promoter, depending on the cellular context. The present review explores the structure and regulatory mechanisms of COUP‑TFII, its functions and molecular mechanisms in CVDs and CRC, and its emerging role in linking these diseases, offering insights into potential treatments and future research directions.
Keywords: COUP‑TFII; CRC; CVD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

