The Influence of Schwann Cell Metabolism and Dysfunction on Axon Maintenance
- PMID: 40709573
- PMCID: PMC12541898
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.70071
The Influence of Schwann Cell Metabolism and Dysfunction on Axon Maintenance
Abstract
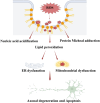
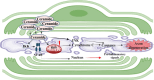
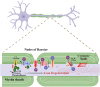
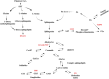
Schwann cells are the glial cells in the peripheral nervous system responsible for the production of myelin, which is essential for rapid, saltatory conduction in nerves. However, it has become increasingly recognized that Schwann cells are also key regulators of neuron viability and function, especially for sensory neurons. Neurons and Schwann cells form a tightknit, interdependent couple with complex mechanisms of communication that are only beginning to be understood. There is growing evidence that Schwann cell metabolism profoundly influences axons through the release of a variety of metabolites. These glial cells serve as energy depots for axon function, supplying lactate and/or pyruvate during repeated firing and after injury. Lipid metabolism in Schwann cells, which is critical for myelin production, also affects axon viability, such that disruptions in the production or breakdown of lipids can lead to axon dysfunction and subsequent degeneration. Here, we discuss emerging concepts on the mechanisms by which Schwann cell metabolites influence neuron activity and survival, with particular focus on how dysfunction of lipid metabolism can lead to axon degeneration and the development of peripheral neuropathy.
Keywords: Schwann cell; axon; myelin.
© 2025 The Author(s). GLIA published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Azhary, H. , Farooq M. U., Bhanushali M., Majid A., and Kassab M. Y.. 2010. “Peripheral Neuropathy: Differential Diagnosis and Management.” American Family Physician 81, no. 7: 887–892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

