Global geographic and socioeconomic disparities in COVID-associated acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40709582
- PMCID: PMC12290987
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.15.04166
Global geographic and socioeconomic disparities in COVID-associated acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and severe complication of COVID-19, which significantly increases the risk of mortality. There has been a wide range of AKI prevalence reported throughout the pandemic, reflecting differences in geographic location, patient characteristics, and health care resources. We aimed to provide a global overview of the COVID-19 AKI prevalence reported in published studies to uncover geographic and socioeconomic disparities.
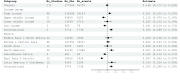
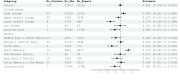
Methods: We undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis, searching PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library for full-text articles published in English reporting the prevalence of AKI from January 2020 to November 2023. All studies defined AKI according to the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes criteria. Clinical characteristics were extracted and examined from 334 studies that met the inclusion criteria. With significant study heterogeneity, random-effect models were estimated. We reported pooled AKI prevalence by country, region, and income level. Meta-regression further examined the relationship between COVID-associated AKI and geographic location.
Results: After removing studies that utilised the same data, 345 796 patients from 246 studies were included, covering 49 countries. Of 246 studies, 137 came from high-income countries, whereas only three were conducted in low-income countries. Among non-intensive care unit (ICU) patients, low-income countries had the lowest COVID-19 AKI prevalence (14.1%; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 11.4-17.2). Among ICU patients, lower-middle-income countries had the lowest COVID-19 AKI prevalence (27.9%;95% CI = 19.4-38.4).
Conclusions: Our study shows significant geographic and socioeconomic disparities in the prevalence of COVID-associated AKI, with a higher prevalence in high-income countries and a lower prevalence in low- and lower-middle-income countries. This study is the most comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis highlighting global disparities in COVID-associated AKI prevalence. Further studies are needed to explain the reasons behind these differences.
Copyright © 2025 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of interest: The authors completed the ICMJE Disclosure of Interest Form (available upon request from the corresponding author) and disclose no relevant interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 30;1(1):CD006207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715243 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
