Deep Learning-Based Landmark Detection Model for Multiple Foot Deformity Classification: A Dual-Center Study
- PMID: 40709679
- PMCID: PMC12303672
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2024.0246
Deep Learning-Based Landmark Detection Model for Multiple Foot Deformity Classification: A Dual-Center Study
Abstract
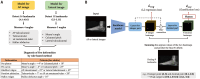
Purpose: To introduce heatmap-in-heatmap (HIH)-based model for automated diagnosis of foot deformities using weight-bearing foot radiographs, aiming to address the labor-intensive and variable nature of manual diagnosis.
Materials and methods: From January 2004 to September 2022, a dual-center retrospective study was conducted. In the first center, 1561 anterior-posterior (AP) and 1536 lateral images from 806 patients were used for model training, while 374 AP and 373 lateral images from 196 patients were allocated to the validation set. For external validation at the second center, 527 AP and 529 lateral images from 270 patients were allocated. Five deformities were diagnosed using four and three angles between the predicted landmarks in the AP and lateral images, respectively. The results were compared with those of the baseline model (FlatNet).
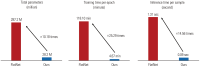
Results: The HIH model demonstrated robust performance in diagnosing multiple foot deformities. On the test set, it outperformed FlatNet with higher accuracy (FlatNet vs. HIH: 78.9% vs. 85.1%), sensitivity (78.9% vs. 84.1%), specificity (79.0% vs. 85.9%), positive predictive value (77.3% vs. 84.4%), and negative predictive value (80.5% vs. 85.7%). Additionally, HIH exhibited significantly lower absolute pixel and angle errors, lower normalized mean errors, higher successful detection rate, faster training and inference speeds, and fewer parameters.
Conclusion: The HIH model showed robust performance in diagnosing multiple foot deformities with high efficacy in internal and external validation. Our approach is expected to be effective for various tasks using landmarks in medical imaging.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; deep learning; diagnostic imaging; foot deformities.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Yildiz K, Cetin T. Interobserver reliability in the radiological evaluation of flatfoot (pes planus) deformity: a cross-sectional study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;61:1065–1070. - PubMed
-
- Ryu SM, Shin K, Shin SW, Lee S, Kim N. Enhancement of evaluating flatfoot on a weight-bearing lateral radiograph of the foot with U-Net based semantic segmentation on the long axis of tarsal and metatarsal bones in an active learning manner. Comput Biol Med. 2022;145:105400. - PubMed
-
- Ryu SM, Shin K, Shin SW, Lee SH, Seo SM, Cheon SU, et al. Automated landmark identification for diagnosis of the deformity using a cascade convolutional neural network (FlatNet) on weight-bearing lateral radiographs of the foot. Comput Biol Med. 2022;148:105914. - PubMed
-
- Ryu SM, Shin K, Shin SW, Lee SH, Seo SM, Cheon SU, et al. Automated diagnosis of flatfoot using cascaded convolutional neural network for angle measurements in weight-bearing lateral radiographs. Eur Radiol. 2023;33:4822–4832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

