Prognostic Role of TSH Within Euthyroid T2DM Patients with Retinopathy: A 3-Year Cohort Study
- PMID: 40710007
- PMCID: PMC12294062
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases13070217
Prognostic Role of TSH Within Euthyroid T2DM Patients with Retinopathy: A 3-Year Cohort Study
Abstract
Background/objectives: We aimed to determine how baseline TSH levels relate to clinical outcomes over a three-year follow-up in euthyroid patients with T2DR.
Methods: This single-center retrospective cohort study included 363 euthyroid T2DR patients who were followed for three years after baseline TSH measurement. Patients were stratified into tertiles based on TSH values belonging to the standard clinical limits (0.35-4.50 mIU/L). Binary and multivariate logistic regression analyses, along with non-linear modeling, were used to evaluate the prognostic impact of TSH and its interaction with age on mortality. The study adhered to the STROBE guidelines.
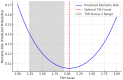
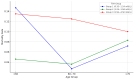
Results: In the first year of follow-up, Group 1 (TSH 0.35-1.24 mIU/L) had significantly higher rates of mortality and combined outcomes compared to Group 2 (TSH 1.24-1.94 mIU/L; p = 0.025 and p = 0.041, respectively). Group 2 had a lower risk (OR for mortality = 0.349, p = 0.004; OR for combined outcome = 0.358, p = 0.007). Between TSH and TSH tertiles, a non-linear, inverted U-shaped relationship was observed, with the lowest mortality risk near 2.0 mIU/L. A significant interaction between TSH and age was found for third-year mortality (p = 0.016).
Conclusions: TSH values showed a non-linear association with outcomes in euthyroid T2DR patients. Group 2 was linked to the lowest risk. Given the significantly higher mortality and combined complications identified within Group 1, closer monitoring and individualized follow-up strategies may be warranted for these patients. Additionally, TSH's impact on long-term mortality increased with age, supporting its use alongside age for risk stratification in T2DR.
Keywords: hormonal biomarkers; non-linear association; risk stratification; short-term prognosis; thyrotropin reference range.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
The Prognostic Potential of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 for Cardiovascular Complications in Peripheral Artery Disease.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Jul 1;12(7):253. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12070253. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40710778 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis of adults and children following a first unprovoked seizure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 23;1(1):CD013847. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013847.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36688481 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khin P.P., Lee J.H., Jun H.-S. Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2023;21:1721727X231154152. doi: 10.1177/1721727X231154152. - DOI
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

