Efficacy of Dupilumab in a Young Woman with Refractory Cutaneous Lichen Planus: A Case-Based Review
- PMID: 40710015
- PMCID: PMC12293882
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases13070225
Efficacy of Dupilumab in a Young Woman with Refractory Cutaneous Lichen Planus: A Case-Based Review
Abstract
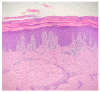
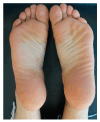
Background: Cutaneous lichen planus (CLP) is a chronic inflammatory T cell-mediated disease driven by a mixed Th1 and Th2 lymphocyte population, for which many of the currently available treatments have poor efficacy. Aim: The aim of this study was to indicate the clinical success of dupilumab administration after two years of treatment in a case of longstanding CLP and to perform a review of the medical literature related to the use of dupilumab in different dermatologic settings and in CLP. Case presentation: One 26-year-old woman with a previous history of atopic dermatitis had a long-lasting skin condition, referred to as a suspected lichen, which started when she was 7 years old. Her disease exhibited a relapsing-remitting course with severe bouts of pruritus over a very long period. The final histological diagnosis of CLP was confirmed at the age of 26. Starting dupilumab (injected subcutaneously at a dose of 600 mg followed by a maintenance dose of 300 mg every two weeks) resolved the skin scenery of this patient, who is currently in full remission. Conclusions: The remarkable recovery from CLP obtained via treatment with dupilumab in this single-patient case study emphasizes the potential therapeutic implications of targeting the Th2 pathway in this skin disorder.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; cutaneous lichen planus; dupilumab; innovative biotechnologies; personalized treatment; pruritus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid Itch Improvement and Skin Clearance with Upadacitinib Versus Placebo (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2) and Versus Dupilumab (Heads Up): Results from Three Phase 3 Clinical Trials in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025 Aug;15(8):2061-2076. doi: 10.1007/s13555-025-01443-w. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40457140 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa is associated with glycolytically active GATA3+ T helper 2 cells which may contribute to pruritus in lesional skin.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jul 16;191(2):252-260. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae110. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38477474
-
Systemic treatments for eczema: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 14;9(9):CD013206. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013206.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32927498 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab Provides Acceptable Safety and Sustained Efficacy for up to 4 Years in an Open-Label Study of Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022 May;23(3):393-408. doi: 10.1007/s40257-022-00685-0. Epub 2022 May 3. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35503163 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of dupilumab in chronic prurigo and chronic idiopathic pruritus: a systematic review of current evidence and analysis of response predictors.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022 Sep;36(9):1541-1551. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18221. Epub 2022 May 31. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022. PMID: 35569006
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

