A New Sensing Platform Based in CNF-TiO2NPs-Wax on Polyimide Substrate for Celiac Disease Diagnostic
- PMID: 40710081
- PMCID: PMC12293545
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15070431
A New Sensing Platform Based in CNF-TiO2NPs-Wax on Polyimide Substrate for Celiac Disease Diagnostic
Abstract
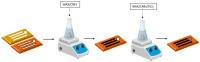
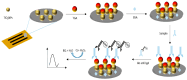
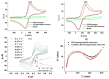
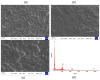
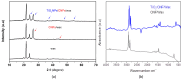
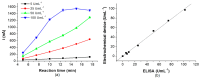
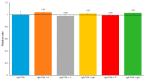
Celiac disease (CD), a human leukocyte antigen-associated disorder, is caused by gluten sensitivity and is characterized by mucosal alterations in the small intestine. Currently, its diagnosis involves the determination of serological markers. The traditional method for clinically determining these markers is the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. However, immunosensors offer sensitivity and facilitate the development of miniaturized and portable analytical systems. This work focuses on developing an amperometric immunosensor for the quantification of IgA antibodies against tissue transglutaminase (IgA anti-TGA) in human serum samples, providing information on a critical biomarker for CD diagnosis. The electrochemical device was designed on a polyimide substrate using a novel solid ink of wax and carbon nanofibers (CNFs). The working electrode microzone was defined by incorporating aminofunctionalized TiO2 nanoparticles (TiO2NPs). The interactions and morphology of CNFs/wax and TiO2NPs/CNFs/wax electrodes were assessed through different characterization techniques. Furthermore, the device was electrochemically characterized, demonstrating that the incorporation of CNFs into the wax matrix significantly enhanced its conductivity and increased the active surface area of the electrode, while TiO2NPs contributed to the immunoreaction area. The developed device exhibited remarkable sensitivity, selectivity, and reproducibility. These results indicate that the fabricated device is a robust and reliable tool for the precise serological diagnosis of CD.
Keywords: celiac disease diagnosis; electrochemical; immunosensor; nanomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
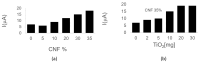
Similar articles
-
Gluten-Associated Medical Problems.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30860740 Free Books & Documents.
-
Rapid Detection of Chlorpheniramine Maleate in Human Blood and Urine Samples Based on NiCoP/PVP/PAN/CNFs Electrochemiluminescence Sensor.Molecules. 2025 Jun 16;30(12):2603. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122603. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572566 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of Celiac Disease in Pediatric Patients With Chronic Diarrhea.Cureus. 2025 May 19;17(5):e84428. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84428. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40539154 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of IgA Anti-Transglutaminase Assessed by Chemiluminescence: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 26;16(15):2427. doi: 10.3390/nu16152427. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125307 Free PMC article.
-
Health effects of exposure to carbon nanofibers: systematic review, critical appraisal, meta analysis and research to practice perspectives.Sci Total Environ. 2009 Jun 1;407(12):3686-701. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.12.025. Epub 2009 Mar 21. Sci Total Environ. 2009. PMID: 19303626
References
-
- Bottari F., Moretto L.M., Ugo P. Impedimetric sensing of the immuno-enzymatic reaction of gliadin with a collagen-modified electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2018;97:51–55. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2018.10.011. - DOI
-
- Bećirević T., Kozarić S., Đugum A., Čović S. Presence of HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8/DR4 celiac disease predisposing alleles in tested group of patients in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Genet. Appl. 2023;7:45–48. doi: 10.31383/ga.vol7iss2ga06. - DOI
-
- DaFonte T.M., Gleeson E., Morson T., Olshan K.L., Moran C.J., Leonard M.M. No Increased risk of taking additional intestinal mucosal research biopsies from the duodenum during pediatric endoscopy. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023;76:480–482. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000003723. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

