Heavy Metal Ion Detection Based on Lateral Flow Assay Technology: Principles and Applications
- PMID: 40710088
- PMCID: PMC12293460
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15070438
Heavy Metal Ion Detection Based on Lateral Flow Assay Technology: Principles and Applications
Abstract
Heavy metal ions pose a significant threat to the environment and human health due to their high toxicity and bioaccumulation. Traditional instrumentations, although sensitive, are often complex, costly, and unsuitable for on-site rapid detection of heavy metal ions. Lateral flow assay technology has emerged as a research hotspot due to its rapid, simple, and cost-effective advantages. This review summarizes the applications of lateral flow assay technology based on nucleic acid molecules and antigen-antibody interactions in heavy metal ion detection, focusing on recognition mechanisms such as DNA probes, nucleic acid enzymes, aptamers, and antigen-antibody binding, as well as signal amplification strategies on lateral flow testing strips. By incorporating these advanced technologies, the sensitivity and specificity of lateral flow assays have been significantly improved, enabling highly sensitive detection of various heavy metal ions, including Hg2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Cr3+. In the future, the development of lateral flow assay technology for detection of heavy metal ions will focus on multiplex detection, optimization of signal amplification strategies, integration with portable devices, and standardization and commercialization. With continuous technological advancements, lateral flow assay technology will play an increasingly important role in environmental monitoring, food safety, and public health.
Keywords: antigen–antibody; environmental monitoring; food safety; heavy metal ion detection; lateral flow assay; nucleic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
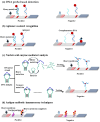
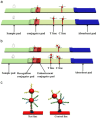
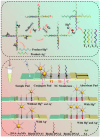
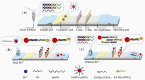
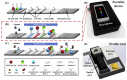

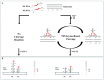
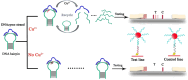


References
-
- Koller M., Saleh H.M. Introductory chapter: Introducing heavy metals. HMs. 2018;1:3–11.
-
- Igwe E., Onoja S., Nwodo P., Baharane V., Diakite S., Saquee F., Ugwu B., Amechi O., Niambe O., Shaibu O. Identification of sources of some priority heavy metallic pollutants caus-ing environmental degradation and it’s health implications. J. Ind. Pollut. Control. 2023;39:1–13.
-
- Tiwari S.M. Impact of heavy metal pollution on the biotic and abiotic components of the environment. South Asian J. Res. Microbiol. 2023;13:38–54.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

