Polymeric Composite-Based Electrochemical Sensing Devices Applied in the Analysis of Monoamine Neurotransmitters
- PMID: 40710090
- PMCID: PMC12293634
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15070440
Polymeric Composite-Based Electrochemical Sensing Devices Applied in the Analysis of Monoamine Neurotransmitters
Abstract
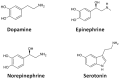
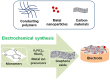
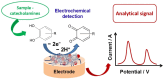
Electroanalysis of monoamine neurotransmitters is a useful tool for monitoring relevant neurodegenerative disorders and diseases. Electroanalysis of neurotransmitters using analytical devices consisting of electrodes modified with tailored and nanostructured composite materials is an active research topic nowadays. Nano- and microstructured composite materials composed of various organic conductive polymers, metal/metal oxide nanoparticles, and carbonaceous materials enable an increase in the performance of electroanalytical sensing devices. Synergistic properties resulting from the combination of various pristine nanomaterials have enabled faster kinetics and increased overall performance. Herein, recent results related to the design and elaboration of electroanalytical sensing devices based on cost-effective and reliable nano- and microstructured composite materials for the quantification of monoamine neurotransmitters are presented. The discussion focuses on the fabrication procedures and detection strategies, highlighting the capabilities of the analytical platforms used in the determination of relevant analytes. The review aims to present the main benefits of using composite nanostructured materials in the electroanalysis of monoamine neurotransmitters.
Keywords: conducting polymers; dopamine; electrochemical sensors; epinephrine; medical applications; metal nanoparticles; nanomaterials; neurotransmitters; serotonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A critical review of electrochemical and optical Vitamin B6 sensing: evolution of biosensor platforms based on advanced nanosystems.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025;65(22):4243-4263. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2386037. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39115011 Review.
-
The Role of Nanomaterials in the Wearable Electrochemical Glucose Biosensors for Diabetes Management.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jul 14;15(7):451. doi: 10.3390/bios15070451. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress in electrochemical assessment of DNA based on nanostructured sensors.Biomed Microdevices. 2025 Jul 12;27(3):36. doi: 10.1007/s10544-025-00763-0. Biomed Microdevices. 2025. PMID: 40650825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shifting paradigm in electrochemical biosensing matrices comprising metal organic frameworks and their composites in disease diagnosis.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024 Jul-Aug;16(4):e1980. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1980. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38973017 Review.
-
Highly Selective Electrochemical Detection of Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone) in Simulated Blood Serum Using Bimetallic Cu/Ni-MOF Decorated CNT Composite on Nickel Foam.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 Jul 21;8(7):5670-5679. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00325. Epub 2025 Jun 13. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 40514770
References
-
- Baranwal J., Barse B., Gatto G., Broncova G., Kumar A. Electrochemical sensors and their applications: A review. Chemosensors. 2022;10:363. doi: 10.3390/chemosensors10090363. - DOI
-
- Bard A.J., Faulkner L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications. 2nd ed. Wiley; New York, NY, USA: 2001.
-
- Pan C., Wei H., Han Z., Wu F., Mao L. Enzymatic electrochemical biosensors for in situ neurochemical measurement. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020;19:162–167. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2019.12.008. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

