Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors for Toxins, Foodborne Pathogens, Pesticides, and Antibiotics Detection: Recent Advances and Challenges in Food Analysis
- PMID: 40710117
- PMCID: PMC12293878
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15070468
Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors for Toxins, Foodborne Pathogens, Pesticides, and Antibiotics Detection: Recent Advances and Challenges in Food Analysis
Abstract
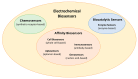
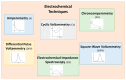
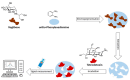
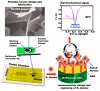
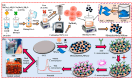
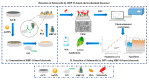
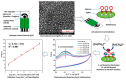
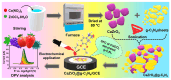
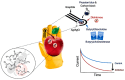
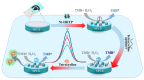
Food safety plays an important and fundamental role, primarily for human health and certainly for the food industry. In this context, developing efficient, highly sensitive, safe, inexpensive, and fast analytical methods for determining chemical and biological contaminants, such as electrochemical (bio)sensors, is crucial. The development of innovative and high-performance electrochemical (bio)sensors can significantly support food chain monitoring. In this review, we have surveyed and analyzed the latest examples of electrochemical (bio)sensors for the analysis of some common biological contaminants, such as toxins and pathogenic bacteria and chemical contaminants, such as pesticides, and antibiotics.
Keywords: antibiotics; electrochemical biosensors; food; foodborne pathogens; pesticides; safety; toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Global Strategy for Food Safety 2022–2030: Towards Stronger Food Safety Systems and Global Cooperation. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2022. [(accessed on 24 March 2025)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240057685.
-
- International Finance Corporation . Food Safety Handbook: A Practical Guide for Building a Robust Food Safety Management System. World Bank; Washington, DC, USA: 2020. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

