Analysis of Implant Osseointegration, Bone Repair, and Sinus Mucosa Integrity Using Bio-Oss® and Hyaluronic Acid-Polynucleotide Gel (Regenfast®) in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation in Rabbits
- PMID: 40710138
- PMCID: PMC12293758
- DOI: 10.3390/dj13070293
Analysis of Implant Osseointegration, Bone Repair, and Sinus Mucosa Integrity Using Bio-Oss® and Hyaluronic Acid-Polynucleotide Gel (Regenfast®) in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation in Rabbits
Abstract
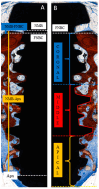
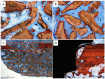
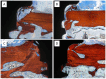
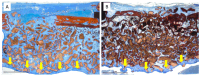
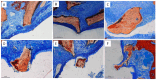
Background: The combination of polynucleotides and hyaluronic acid with bovine bone grafts in maxillary sinus lift procedures appears to be a promising strategy to enhance bone regeneration. This study aimed to analyze implant osseointegration, bone repair and sinus mucosa integrity using Bio-Oss® and Hyaluronic Acid-Polynucleotide Gel (Regenfast®) in maxillary sinus augmentation in rabbits. Methods: Sinus floor elevation was performed in 12 rabbits, with one implant placed per sinus simultaneously. In the control group, sinuses were grafted with deproteinized bovine bone mineral (Bio-Oss®) alone; in the test group, Bio-Oss® was combined with Regenfast®. Two histological slides were obtained per sinus after 2 weeks (six animals) and 10 weeks (six animals): one from the grafted area alone (non-implant sites), and one from the implant site. Primary outcome variables included the percentage of newly formed bone, the extent of implant osseointegration, and the number of sinus mucosa perforations caused by contact with graft granules. Results: After 10 weeks of healing, the test group showed a significantly higher percentage of new bone formation (37.2 ± 6.7%) compared to the control group (26.8 ± 10.0%; p = 0.031); osseointegration extended to the implant apex in both groups; fewer sinus mucosa perforations were observed in the test group (n = 5) than in the control group (n = 14). Conclusions: The addition of Regenfast® to Bio-Oss® granules promoted enhanced bone regeneration within the elevated sinus area and was associated with a lower incidence of sinus membrane perforations compared to the use of Bio-Oss® alone.
Keywords: animal study; bone healing; dental implants; histology; hyaluronic acid; osseointegration; osteoinduction; resorbable polynucleotides; sinus augmentation; sinus membrane perforation; xenogeneic bone substitute.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: bone augmentation techniques for dental implant treatment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD003607. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003607.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 07;(4):CD003607. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003607.pub4. PMID: 18646092 Updated.
-
On the Use of a Sticky Bone Substitute in the Presence of a Ruptured Sinus Membrane During Sinus Elevation Procedures: An Experimental Rabbit Study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2025 Jul 25;40(4):417-426. doi: 10.11607/jomi.11011. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2025. PMID: 39365907
-
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 13;2014(5):CD008397. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008397.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24825543 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential Bone Repair in Rabbit Sinus Lifts Using Bio-Oss and Hyaluronic Acid-Polynucleotide Gel (Regenfast).J Funct Biomater. 2024 Nov 28;15(12):361. doi: 10.3390/jfb15120361. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39728161 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review.Ann Periodontol. 2003 Dec;8(1):328-43. doi: 10.1902/annals.2003.8.1.328. Ann Periodontol. 2003. PMID: 14971260
References
-
- Bouwman W.F., Eijsackers F.A., Bravenboer N., Ten Bruggenkate C.M., Remmelzwaal S., Schulten E.A.J.M. Long-Term Bone Height Changes After Sinus Floor Elevation With Maxillary or Mandibular Bone Grafts: A Radiological Study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2025;27:e70008. doi: 10.1111/cid.70008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zijderveld S.A., Schulten E.A., Aartman I.H., ten Bruggenkate C.M. Long-term changes in graft height after maxillary sinus floor elevation with different grafting materials: Radiographic evaluation with a minimum follow-up of 4.5 years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009;20:691–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01697.x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

